|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
In which of the following reactions will the equilibrium shift to the left when the pressure on the system is decreased?
I. 2H2 + O2 ↔ 2H2O
II. 2CO + O2 ↔ 2CO2
III. 2MgO(s) ↔ 2Mg(s) + O2(g) |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II only |
C
|
I and II only |
D
|
I and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Stoichiometry | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following reaction has a negative change in enthalpy: 2NO(g)+O2(g) <-->2NO2(g). Which of the following would increase the ratio of NO2 to NO at equilibrium? |
|
A
|
Decreasing the volume of the system. |
B
|
Inserting a catalyst. |
C
|
Removing oxygen from the system. |
D
|
Increasing the temperature. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Assuming the equilibrium of the following system at 25 °C is -3.8 kcal/mol, which of the following actions would shift the equilibrium to the right?
H3PO4(s) ↔ 3H+ + PO4- |
|
A
|
increasing the temperature of the system |
B
|
decreasing the temperature of the system |
C
|
adding HCl to the mixture |
D
|
adding Na3PO4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction will surely be nonspontaneous if |
|
A
|
Heat is released and entropy increases |
B
|
Heat is absorbed and entropy increases |
C
|
Heat is released and entropy decreases |
D
|
Heat is absorbed and entropy decreases |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction can be guaranteed to be spontaneous if |
|
A
|
ΔG>0 |
B
|
ΔH<0 and ΔS>0 |
C
|
ΔH>0 and ΔS>0 |
D
|
ΔH>0 and ΔS<0 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
All of the following are processes which increase the entropy of a system except: |
|
A
|
Hydrolysis |
B
|
Amino acid synthesis |
C
|
Anaerobic respiration |
D
|
Evaporation of a liquid |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A system in chemical equilibrium |
|
A
|
ceases to undergo any reaction |
B
|
has a balance of the forward and reverse reactions |
C
|
goes forward until all reactants are consumed |
D
|
goes forward until all reactants are consumed, then reverses until all energy is lost |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
An alcohol that is placed in concentrated acid and heat forms equilibrium with what? |
|
A
|
alkyne + water |
B
|
alkene + water |
C
|
alkyne + alkane |
D
|
alkane + alkene |
|
|
|
Tags:
Alcohols | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
Increasing the temperature in an exothermic reaction will: |
|
A
|
shift the equilibrium right. |
B
|
shift the equilibrium left. |
C
|
have no effect on the reaction. |
D
|
shift the equilibrium to the left or the right depending on the catalyst used. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the following information:
Au3+ + 3e- → Au E° = 1.50 V
Cu 2+ + 2e- → Cu E° = 0.34 V
What is the standard potential of the following reaction? Is it spontaneous?
2Au + 3Cu2+ → 2Au3+ + 3Cu |
|
A
|
1.16 V, spontaneous |
B
|
-1.16 V, non-spontaneous |
C
|
1.98 V, spontaneous |
D
|
-1.98 V, non-spontaneous |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrochemistry | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
An alkene with water will be in equilibrium with the alcohol that results from the hydration of the alkene by the water. With dilute acid and low temperatures, this equilibrium would be driven in which direction? |
|
A
|
To the alkene and water |
B
|
To the alcohol |
C
|
Neither side |
D
|
The direction of favoured equilibrium cannot be determined |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Alcohols | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
If an exothermic reaction is heated, the equilibrium will shift in which direction? |
|
A
|
towards the products |
B
|
towards the reactants |
C
|
neither |
D
|
it depends on the value of the individual k constants |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
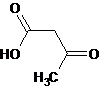
In beta-keto acid decarboxylation reaction of acetoacetic acid in water, the percent yield of the reaction can be increased by which of the following steps?
|
|
A
|
Adding acetoacetic acid |
B
|
Adding carbon dioxide |
C
|
Removing acetone |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
An exothermic reaction at equilibrium whose pressure is increased but temperature remains constant will |
|
A
|
shift towards the products |
B
|
shift towards the reactants |
C
|
not be affected |
D
|
the answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
In order to make a compound AB, the following reaction is used, which yields 411 kJ of energy for each mole of AB made. Which of the following statements would lead to more AB being made?
A(aq) + 1/2 B2(aq) ↔ AB(aq) |
|
A
|
Reducing the heat at which the reaction takes place |
B
|
Removing 1 mol of A from the reaction |
C
|
Increasing the pressure at which the reaction takes place |
D
|
Increasing the size of the container in which the reaction occurs |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
For a particular reaction, the ratio of the forward rate over the reverse rate is measured (forward rate / reverse rate). Which of the following will most increase this quotient? |
|
A
|
Include a catalyst. |
B
|
Add thermal energy to the system. |
C
|
Remove thermal energy from the system. |
D
|
None of the above. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
In following reaction, what is the correct equilibrium equation?
FeO3(s) + 3CO(g) ↔ Fe(l) + 3CO2(g) |
|
A
|
K = [CO2]3/[CO]3 |
B
|
K = [CO]3/[CO2]3 |
C
|
K = [CO2]3[Fe]/[CO]3[FeO3] |
D
|
K = [CO]3[FeO3]/[CO2]3[Fe] |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
Sodium hypochlorite, NaClO, is highly soluble in water and decomposes to liberate O2(g). What would happen to the freezing point of a 0.05 M solution of sodium hypochlorite after it has completely decomposed? |
|
A
|
The freezing point would increase because the molarity of the solution would decrease. |
B
|
The freezing point would remain the same because the molarity of the solution would be unchanged. |
C
|
The freezing point would decrease because the molarity of the solution would increase. |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined from the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Solutions | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ethanol (alcohol) is metabolized in the body through several important enzymes. Ethanol is converted to acetaldehyde via alcohol dehydrogenase, from which it is converted to acetic acid by aldehyde dehydrogenase. Inefficiency of the aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme can result in a buildup of intermediates, resulting in headache, red flushing of the face, and other negative effects. Acetic acid can finally be converted to acetyl CoA by a separate enzyme. Which of the following is true regarding this phenomenon? |
|
A
|
It can be alleviated through an increase in amount of alcohol dehydrogenase. |
B
|
In populations which experience these symptoms due to enzyme inefficiency, there is a decrease in the overall concentration of acetaldehyde. |
C
|
The end-products of ethanol metabolism can enter glycolysis to create ATP. |
D
|
There would be decreased acetic acid concentrations in people with this enzyme inefficiency. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Using the standard half-cell potentials for the reactions below, identify the reaction which will be spontaneous.
Ba2+ + 2e- ↔ Ba -2.90 V
Mn2+ + 2e- ↔ Mn -1.04 V
K+ + e- ↔ K -2.92 V
2H+ + 2e- ↔ H2 0.00 V
I3- + 2e- ↔ 3I- 0.53 V |
|
A
|
Ba2+ + Mn ↔ Mn2+ + Ba |
B
|
K + Ba2+ ↔ K+ + Ba |
C
|
3I- + 2H+ ↔ I3- + H2 |
D
|
K+ + I3- ↔ 3I- + K |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrochemistry | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
The quantity of Ba(OH)2 that dissolves in water can be increased with the addition of which of the following? |
|
A
|
NaOH |
B
|
HCl |
C
|
NH4OH |
D
|
NH3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
For a given spontaneous equilibrium reaction, which of the following statements is true? |
|
A
|
The reaction will start without the input of energy. |
B
|
There is a net input of energy into the reaction from the environment. |
C
|
The standard potential for the reaction is negative. |
D
|
The equilibrium constant K will be greater than 1. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
The reversible chemical reaction A + B ↔ C is an exothermic reaction and has a Keq of 2 x 10-2. This reaction can be driven to completion by which of the following methods? |
|
A
|
Addition of a catalyst. |
B
|
Increase in the temperature of the reaction. |
C
|
Removal and collection of product from the reaction. |
D
|
Reversible reactions cannot be driven to completion. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction, A + 2B → C + D takes place in a chamber. 5 moles of A and 12 moles of B are mixed together to produce 3 moles of C at equilibrium. Assuming all of the reactants and products are in aqueous solution and volume remains constant, what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
The formation of Al2O3 in the reaction below is an example of which type of reaction?
2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe |
|
A
|
combination reaction |
B
|
combustion reaction |
C
|
single replacement reaction |
D
|
double replacement reaction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous General Chemistry | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following describes a chemical reaction which has a negative ΔG? |
|
A
|
Endergonic |
B
|
Exergonic |
C
|
Enzyme-catalyzed
|
D
|
The reaction is at equilibrium
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT true regarding an endothermic chemical reaction such as joining together glucose and fructose to form sucrose? |
|
A
|
The reaction requires an input of energy
|
B
|
With a large amount of entropy, an exergonic reaction can result |
C
|
The reaction releases energy
|
D
|
The energy used in bond-breaking reactions is greater than the energy released in bond-making products |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following influences a chemical reaction to become spontaneous? |
|
A
|
Reactants having lower free energy than the products
|
B
|
Reactants being more ordered than the products
|
C
|
Keq < 1
|
D
|
Low reaction temperature
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Reactions A and B are unrelated and each has its equilibrium constant measured. Reaction A has K = 4 x 102 and Reaction B as K = 2.8 x 10-1. Which of the following statements must hold true given this information? |
|
A
|
The forward reaction rate of A is greater than the forward reaction rate of B. |
B
|
The forward reaction rate of B is greater than the forward reaction rate of A. |
C
|
The reverse reaction rate of A is greater than the forward reaction rate of B. |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Chatelier's principle is used to predict what happens to a chemical equilibrium upon a change in conditions. Which of the following is NOT an example of a reaction that correctly readjusts itself to a change in conditions? |
|
A
|
The amount of product increases if the concentration of a reactant increases. |
B
|
Given a reversible exothermic reaction that produces ammonia, less ammonia is produced if the temperature is increased. |
C
|
Given a reaction that produces ammonia, more ammonia is produced upon the addition of a catalyst. |
D
|
Given a reaction that changes from 2 total gas moles of reactants to 1 total gas mole of product, the equilibrium shifts to the reactant side if the volume is increased. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
The reaction below has a ΔH > 0 and an equilibrium pressure of 2 atm. Which of the following will shift the reaction to the left at equilibrium?
CO2 (g) → CO (g) + 1/2 O2 (g)
I. Increase volume
II. Decrease volume
III. Decrease temperature |
|
A
|
I only
|
B
|
II only
|
C
|
I and III only
|
D
|
II and III only
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Gases | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true of a reversible reaction where Q > K? |
|
A
|
The reaction is at equilibrium. |
B
|
The reaction will increase the concentration of products over time. |
C
|
The reaction will increase the concentration of reactants over time. |
D
|
The reaction will be at equilibrium once the activation energy is reached. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
An equilibrium reaction will be shifted towards the products when the temperature is increased if: |
|
A
|
the concentration of products is greater than the concentration of reactants. |
B
|
the concentration of reactants is greater than the concentration of products. |
C
|
the reaction is exothermic. |
D
|
the reaction is endothermic. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
At 1 atm and 25 degrees celcius, what are the units on Kw, the dissociation constant of water? |
|
A
|
unitless |
B
|
M |
C
|
M2 |
D
|
mol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction is as follows: 3X5 --> 5X3 where X is a particular atom. This reaction reaches equilibrium at particular settings in a closed container. What would happen if the volume of the container were to suddenly be increased? |
|
A
|
the reaction would tend towards the products |
B
|
the reaction would tend towards the reactants |
C
|
the reaction would stay in the same equilibrium |
D
|
knowledge of temperature and pressure of the system would be required to assess changes in equilibrium with changes in volume |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|

