|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following has a negative standard free energy change at 25 °C?
I. CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
II. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
III. 2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g) |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II only |
C
|
I and II only |
D
|
II and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following situations will always yield a spontaneous reaction? |
|
A
|
Negative change in heat and negative change in entropy. |
B
|
Positive change in heat and negative change in entropy. |
C
|
Positive change in heat and positive change in entropy. |
D
|
Negative change in heat and positive change in entropy. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Arrange the following substances in terms of increasing molar entropy at standard room temperature and pressure: Ca(s), Cl2(g), Cl2(l), CaCl2(s) |
|
A
|
Cl2(g), Cl2(l), Ca(s), CaCl2(s) |
B
|
Cl2(g), Cl2(l), CaCl2(s), Ca(s) |
C
|
CaCl2(s), Ca(s), Cl2(l), Cl2(g) |
D
|
Ca(s), CaCl2(s), Cl2(l), Cl2(g) |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is decreased when a catalyst is added to a reaction? |
|
A
|
entropy of the system |
B
|
activation energy |
C
|
chemical potential energy |
D
|
kinetic energy |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
In thermodynamics, under what conditions could a spontaneous reaction result a decrease in temperature?
|
|
A
|
the increase in entropy times the absolute temperature is less than the positive value of heat absorbed
|
B
|
the increase in entropy times the absolute temperature is less than the negative value of heat absorbed
|
C
|
the increase in entropy times the absolute temperature is greater than the positive value of heat absorbed
|
D
|
the increase in entropy times the absolute temperature is greater than the negative value of heat absorbed
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a spontaneous process? |
|
A
|
A process where the change in entropy of the system is positive. |
B
|
Two gases in one container maintaining different temperatures. |
C
|
The precipitation of sodium chloride when 1 mole of NaCl is added 2L of water. |
D
|
None of the above. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction has a Gibb's free energy change of -1000 kJ/mol at 500K. If the reaction occurs in a heat engine with a 100K cold reservoir, what is the maximum amount of work that can be done with the reaction per mole? |
|
A
|
1000 kJ |
B
|
800 kJ |
C
|
600 kJ |
D
|
200 kJ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
A substance is dissolved in water, releasing heat. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is measured to be less than 1. What is the sign of standard entropy change for this process? |
|
A
|
Positive |
B
|
Zero |
C
|
Negative |
D
|
Cannot be determined |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
A block of solid water (ice) with a volume of 1 L melts to form liquid water with a volume of
0.92 L. Assume that the system is isothermal, at 0 °C, and ideal. The magnitude of which term
in the Boltzmann definition of entropy has increased? |
|
A
|
Volume |
B
|
Moles |
C
|
Boltzman Coefficient |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A solute is placed inside of a solvent. It is noted that the solute has very strong attractive forces with the solvent. In a plot of Gibbs free energy versus temperature, what can be inferred about the y-intercept of the graph of the pure solvent and the solvent with solute? |
|
A
|
The pure solvent will intersect the y-intercept lower than the impure solvent. |
B
|
The pure solvent will intersect the y-intercept higher than the impure solvent. |
C
|
The pure solvent will intersect the y-intercept at the same level as the impure solvent. |
D
|
There is not enough information to tell. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following does the change in entropy of a system NOT depend on? |
|
A
|
Volume |
B
|
Moles |
C
|
Pressure |
D
|
None of the Above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which statement describes characteristics of an endothermic reaction? |
|
A
|
The sign of H is positive, and the products have less potential energy than the reactants. |
B
|
The sign of H is positive, and the products have more potential energy than the reactants. |
C
|
The sign of H is negative, and the products have less potential energy than the reactants. |
D
|
The sign of H is negative, and the products have more potential energy than the reactants. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Haber process is used to create ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gas. The reaction is as follows: N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) + heat. The reaction occurs in a closed container. What would happen if the temperature of the system was to suddenly drop? |
|
A
|
There would be an increase in the amount of nitrogen gas |
B
|
There would be a larger increase in hydrogen gas than nitrogen gas |
C
|
There would be an increase in the amount of ammonia |
D
|
Temperature would continue to decrease after the initial drop |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction has a positive change in enthalpy and negative change in entropy. The reaction is |
|
A
|
spontaneous |
B
|
non-spontaneous |
C
|
favors the products |
D
|
very fast |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which is a feature of entropy? |
|
A
|
It is defined by the first law of thermodynamics |
B
|
Entropy of a closed system always decreases |
C
|
It is the energy in a thermodynamic system that is not available for work |
D
|
Its unit is the kilowatt-hour |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best describes enthalpy? |
|
A
|
Energy that is not available for work in a thermodynamic system |
B
|
Energy stored in a system derived from its configuration |
C
|
The energy of motion in an object |
D
|
The total energy of a thermodynamic process |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the standard enthalpy of formation (ΔH°) of O2 (g)? |
|
A
|
0 kJ/mol |
B
|
-393.5 kJ/mol |
C
|
-424.8 kJ/mol |
D
|
-528.1 kJ/mol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
At 200 K, Substance X is in the liquid phase. Substance X vaporizes at 400 K and has a heat of vaporization of 49.1 kJ/kg. The heat capacity of Substance X is 640 J/kg*°C. What energy input is required to fully vaporize 1 g of Substance X if its initial temperature is 200 K? |
|
A
|
49.1 J |
B
|
128 J |
C
|
177.1 J |
D
|
49.23 kJ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular enzyme-catalyzed biological reaction (Reaction 1) in humans takes the substrate A and converts it to B. The ΔG is -100 kJ/mol. A different enzyme is later found which also has A as a substrate (Reaction 2). The identity of the product from this different enzyme is not recorded. It is found that the ΔG for this new reaction is -120 kJ/mol. Which of the following holds true? |
|
A
|
Reaction 2 must run faster kinetically than Reaction 1 |
B
|
The second enzyme is more efficient at converting A to B due to the larger decrease in free energy |
C
|
Reactant A can bind to 2 enzymes at a time |
D
|
The product of Reaction 2 cannot be B |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not an example of energy transfer? |
|
A
|
convection |
B
|
conduction |
C
|
radiation |
D
|
induction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
A coffee-cup calorimeter is a simple contraption which utilizes a styrofoam coffee-cup (relatively well-insulated) filled with water, and a thermometer. The cup is filled with 250 g of water and sits at a temperature of 20 °C. A sample is placed in the calorimeter and the heat of the reaction is measured via a thermometer. Which of the following holds true regarding this set up? |
|
A
|
Volume is held constant in such a calorimeter |
B
|
Less energy is needed to raise the current setup 1 °C than heating 150 g of water 2 degrees |
C
|
A bomb calorimeter does not require the utilization of a thermometer |
D
|
None of the above - knowledge of the specific heat capacity of water needs to be given to understand the dynamics of the calorimeter set up |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
An exothermic reaction at equilibrium whose pressure is increased but temperature remains constant will |
|
A
|
shift towards the products |
B
|
shift towards the reactants |
C
|
not be affected |
D
|
the answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
An object is heated with a definite amount of energy P. As it heats, the object expands. Which of the following is true regarding internal energy of the object in this scenario? |
|
A
|
The total energy change of the object is greater than zero but less than P |
B
|
The total energy change of the object is equal to P |
C
|
The total energy change of the object is greater than P |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined from the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
The standard enthalpy of formation of an element in its standard state is always |
|
A
|
less than zero. |
B
|
equal to zero. |
C
|
greater than zero. |
D
|
either less than or greater than zero, but never equal to zero. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following reaction is found to be endothermic: H2(g) + ZnCl2(s) → Zn(s) + 2HCl(l). Which of the following holds true for the reaction? |
|
A
|
It is non-spontaneous |
B
|
It is spontaneous |
C
|
We are missing information to evaluate its spontaneity |
D
|
If the reaction takes place in a closed container, temperature inside the container will increase |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following statements regarding spontaneous reactions is false? |
|
A
|
Once initiated, spontaneous reactions produce energy in excess of their activation energy. |
B
|
Any reaction with a value of ΔG that is negative must be spontaneous. |
C
|
Spontaneous reactions are capable of resulting in entropic decreases. |
D
|
Spontaneous reactions always have sufficient energy to initiate on their own without the need for energy input at initiation. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following describes the entropy change for the following reaction?
3A(g) + 2B(g) → 3C(s) + D(s) |
|
A
|
ΔS < 0 |
B
|
ΔS > 0 |
C
|
ΔS = 0 |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined from the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is false about a chemical reaction which proceeds spontaneously at room temperature? |
|
A
|
The reaction does not have an activation energy. |
B
|
The reaction releases energy to its surroundings. |
C
|
The reaction can be reversible. |
D
|
It is possible for such a reaction to be zero order. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
Certain salts will dissolve into water exothermically while others will dissolve endothermically. Which of the following statements is true regarding the difference between these two categories of salts? |
|
A
|
The exothermically-dissolving salts are spontaneous reactions while the endothermically-dissolving salts are nonspontaneous reactions. |
B
|
The enthalpy change of exothermic reactions is positive while the enthalpy change for endothermic reactions is negative. |
C
|
The temperature of the solution must remain constant for the dissolution reaction to continue spontaneously. |
D
|
The entropy of the solution increases regardless of whether the dissolution is exothermic or endothermic. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the specific heat capacity of an element which requires 80 J to heat 5 g of the element from 25 °C to 35 °C? |
|
A
|
0.125 J/g°C |
B
|
0.250 J/g°C |
C
|
0.457 J/g°C |
D
|
1.60 J/g°C |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the minimum temperature for the decomposition of sodium bicarbonate to be spontaneous if ΔHrxn = 50 kJ/mol and ΔSrxn = 200 J/mol*K? |
|
A
|
0.250 K |
B
|
250 K |
C
|
523 K |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
Oxygen and aluminum have roughly the same heat capacity in units of Jg-1K-1. Based on this information, which of the following statements is FALSE? |
|
A
|
Oxygen and aluminum will have different boiling points despite having the same heat capacity. |
B
|
One liter of oxygen would absorb the same amount of energy as one liter of aluminum for a given temperature increase. |
C
|
Heat capacity is not directly correlated to density. |
D
|
Equal masses of oxygen and aluminum will absorb the same amount of energy for a given temperature increase. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
A carbanion can be stabilized in which of the following ways? |
|
A
|
The addition of halogen atoms to the carbanion's substituent groups. |
B
|
Increasing its solution temperature. |
C
|
The addition of aliphatic groups to the carbanion's substituent groups. |
D
|
Its placement in a nonpolar solvent. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student examines two non-identical objects and measures their temperatures. Object A has a temperature of 70 °C while Object B has a temperature of 85 °C. The student concludes that Object B contains more heat energy. Which of the following correctly assesses the student's conclusion? |
|
A
|
The student's conclusion is correct because hotter objects contain more heat energy than colder objects. |
B
|
The student's conclusion is correct because hotter objects do not always contain more heat energy than colder objects. |
C
|
The student's conclusion is incorrect because hotter objects contain more heat energy than colder objects. |
D
|
The student's conclusion is incorrect because hotter objects do not always contain more heat energy than colder objects. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is TRUE of a material which gains energy over time? |
|
A
|
The temperature of the material rises over time as long as there is a net increase in energy. |
B
|
The temperature of the material will rise only if the energy being added is in the form of heat. |
C
|
The temperature of the material rises over time as long as there is a net increase in energy and no phase change is occurring. |
D
|
As its total energy increases, the material will lose energy to its environment at a decreasing rate. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
A spontaneous chemical reaction has a ΔH° = -879 kJ/mol. Which of the following statements about this reaction is true? |
|
A
|
The reaction rate will be fast because it is spontaneous and exothermic. |
B
|
The reaction rate will depend on the ΔG° of the reaction. |
C
|
The reaction rate will depend on the activation energy of the reaction. |
D
|
The rate of the reaction will increase if the temperature is decreased. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
Dry ice, or solid CO2 sublimes at atmospheric pressure. What prediction can be made about the entropy change during the sublimation of CO2? |
|
A
|
ΔS is positive, entropy decreases |
B
|
ΔS is positive, entropy increases |
C
|
ΔS is negative, entropy decreases |
D
|
ΔS is negative, entropy increases |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
A non-spontaneous reaction with a positive change in enthalpy and entropy can be made spontaneous by |
|
A
|
increasing pressure |
B
|
adding more reactant |
C
|
increasing the temperature |
D
|
the reaction cannot be made spontaneous |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) of the reaction 2NO + O2 → 2NO2 given the following information:
N2 + O2 → 2NO (ΔH = 180 kJ)
N2 + 2O2 → 2NO2 (ΔH = 68 kJ)
|
|
A
|
112 kJ |
B
|
-112 kJ |
C
|
248 kJ |
D
|
-248 kJ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following must be true for a dissolution reaction where the ΔH of the energy required to break the intermolecular bonds of the solute is greater than the ΔH of the energy released in the hydration of the solute? |
|
A
|
The dissolution reaction is exothermic. |
B
|
The dissolution reaction is endothermic. |
C
|
The dissolution reaction is endergonic. |
D
|
The entropy change is negative. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student is performing bomb calorimetry for a combustion reaction. The bomb calorimeter normally holds 5 L of water with a heat capacity of 4.185 J/g•°C. However, the student misread the directions and used 6 L of ethanol which has a heat capacity of 2.423 J/g•°C. If the student calculates the energy released by the reaction assuming it was 5 L of water, what will be the difference between the actual energy of the reaction and the calculated energy? Note: the density of ethanol and water under normal conditions is 0.8 g/mL and 1.0 g/mL, respectively. |
|
A
|
The calculated energy will be higher than the actual energy because the total heat capacity of the calorimeter with ethanol is greater than with water. |
B
|
The calculated energy will be higher than the actual energy because the total heat capacity of the calorimeter with ethanol is less than with water. |
C
|
The calculated energy will be lower than the actual energy because the total heat capacity of the calorimeter with ethanol is greater than with water. |
D
|
The calculated energy will be lower than the actual energy because the total heat capacity of the calorimeter with ethanol is less than with water. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
When an electrode of Au(s) is placed into a solution of PbSO4, no precipitate of Pb forms on the surface of the electrode. Which of the following can be concluded from this information? |
|
A
|
The reaction Au + Pb2+ → Au+ + Pb is spontaneous |
B
|
The E� of the reaction setup is negative |
C
|
An increase in the PbSO4 would cause Pb2+ to plate onto the electrode |
D
|
Reversal of the setup with a solid Pb electrode and aqueous Au would not have Au precipitate onto Pb |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the ΔH°rxn for the reaction
CH4(g) + 4 Cl2(g) → CCl4(g) + 4HCl(g)
Given the following data:
|
ΔH°f (kJ/mol) |
| CH4 |
-75 |
| CCl4 |
-96 |
| HCl |
-92 |
|
|
A
|
-113 kJ |
B
|
-464 kJ |
C
|
-389 kJ |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Arrhenius equation, shown below, is a description of the relationship between the rate constant, k, the activation energy of the reaction, and the temperature in Kelvin.
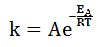
Here, A and R are constants. For ratios of EA/RT that are greater than 1, if the constant R were half of its actual value, what would happen to the rate constant k? |
|
A
|
It would increase by less than double. |
B
|
It would increase by more than double. |
C
|
It would decrease to less than half of its current value. |
D
|
It would decrease to more than half of its current value. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following statements is true regarding a system to which heat energy is added at a constant rate? Assume the system is open and exposed to air. |
|
A
|
The rate of heat loss to the environment is independent of the temperature of the environment. |
B
|
The temperature will rise linearly. |
C
|
The system will reach a maximum temperature when the rate of heat loss is equal to the rate of heat input. |
D
|
The entropy of the system will decrease as the temperature increases. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
Freeze-drying is the process by which water can be removed from materials that have been frozen first. Which of the following enhances the rate at which a material can be dried after being frozen? |
|
A
|
increasing the pressure on the material |
B
|
placing the material in a vacuum |
C
|
further lowering the temperature of the material |
D
|
increasing the humidity of the air in which the material has been placed |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
A spontaneous reaction can also be endothermic as long as which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
The value of TΔS is negative and greater than the value of ΔH |
B
|
The value of TΔS is positive and greater than the value of ΔH |
C
|
The value of TΔS is negative and less than the value of ΔH |
D
|
The value of TΔS is positive and less than the value of ΔH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student measures the temperature of a system as energy is added to it. The temperature rises linearly and over time begins to level off before reaching a plateau. The student notes that energy continues to be added at a constant rate. Which of the following conclusions must be true based on this information? |
|
A
|
The system is not closed, and loses energy to its surroundings. |
B
|
The system is undergoing a phase change and thus it plateus. |
C
|
The electrons of the system have reached their maximum energy state and cannot be excited any further. |
D
|
The scenario is not possible and the student has made a measurement error. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 49 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two biochemical mechanisms use the same reactants to produce the same products. The simplified, balanced reaction for both mechanisms is 2A + B → 2C. If one biochemical mechanism performs the reaction in 2 steps but the other mechanism performs it in 4 steps, how does the net enthalpy change of the reaction differ between the two biochemical mechanisms? |
|
A
|
The enthalpy change for 4 steps is double the enthalpy change for 2 steps |
B
|
The enthalpy change for 4 steps is 4 times more than the enthalpy change for 2 steps |
C
|
The enthalpy change for 4 steps is half the enthalpy change for 2 steps |
D
|
The enthalpy change for 4 steps is the same as the enthalpy change for 2 steps |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
A liquid substance is brought to its freezing point and completely solidified. At a constant temperature, if the pressure on the solid substance is increased, the substance will convert back to a liquid: |
|
A
|
always. |
B
|
only if the solid is denser than the liquid. |
C
|
only if the liquid is denser than the solid. |
D
|
never. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 51 |
Go |
Q:
|
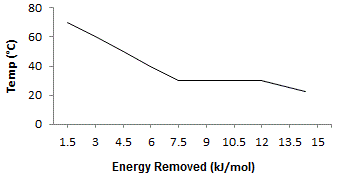
The graph above shows the phase transition of a substance from its liquid to its solid state. What is the ΔHfusion of the substance? |
|
A
|
4.5 kJ/mol |
B
|
6 kJ/mol |
C
|
10.5 kJ/mol |
D
|
40 kJ/mol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
2A (s) + B (l) → 4D (g)
For the exothermic reaction above, which of the following must be true? |
|
A
|
The reaction is spontaneous |
B
|
The reaction has a net decrease in entropy |
C
|
The reaction would not change the pressure if occurring in a closed container |
D
|
The reaction absorbs heat |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 53 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student reports that a reaction has ΔG = -4900 J/mol. The student can successfully report that:
I. The reaction is exothermic
II. The reaction is endothermic
III. The reaction is spontaneous |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
As water evaporates from a surface, the surface cools. This is because: |
|
A
|
water is always at a lower temperature than the surface. |
B
|
the water absorbs energy from the surface for its ΔHvaporization as it evaporates. |
C
|
the presence of water vapor in the air keeps surfaces cool. |
D
|
the concentration of various contaminants increases, increasing the boiling point of the water and requiring more energy from the surface to evaporate. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
Using the information in the table below, calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction:
CS2 + 3 O2 → CO2 + 2 SO2
| Reaction |
Heat of Formation (kJ/mol) |
| C + O2 → CO2 |
-400 |
| S + O2 → SO2 |
-250 |
| C + 2 S → CS2 |
90 |
|
|
A
|
-560 kJ/mol |
B
|
-810 kJ/mol |
C
|
-740 kJ/mol |
D
|
-990 kJ/mol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 56 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction is determined to be spontaneous, with a ΔG° = -412 kJ/mol. Which of the following can be concluded from this reaction? |
|
A
|
The reaction is exothermic |
B
|
The reaction proceeds rapidly at STP |
C
|
The reaction releases free energy to the environment |
D
|
The reaction experiences an increase in entropy |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the potentials of the following half-reactions, how would the net reaction proceed if set up to run as a spontaneous reaction?
| Al3+ + 3e- → Al | E° = -1.66 V |
| Fe3+ + 3e- → Fe | E° = -0.04 V |
|
|
A
|
Al3+ + Fe3+ → Al + Fe |
B
|
Al3+ + Fe → Al + Fe3+ |
C
|
Al + Fe3+ → Fe + Al3+ |
D
|
Al + Fe → Al3+ + Fe3+ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 58 |
Go |
Q:
|
For which of the following combinations of enthalpy and entropy will a reaction be always nonspontaneous? |
|
A
|
change in enthalpy < 0, change in entropy > 0 |
B
|
change in enthalpy > 0, change in entropy < 0 |
C
|
change in enthalpy < 0, change in entropy < 0 |
D
|
change in enthalpy > 0, change in entropy > 0 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 59 |
Go |
Q:
|
A substance is brought to its triple point and the pressure is raised while keeping the temperature constant. The substance will therefore end up in which state? |
|
A
|
gas |
B
|
solid |
C
|
liquid |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 60 |
Go |
Q:
|
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed system:
N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) ↔ 2NH3 (g) ΔH° = -92.6 kJ
Which of the following will favor the formation of NH3? |
|
A
|
Increasing the volume |
B
|
Increasing the temperature |
C
|
Increasing the pressure |
D
|
Decreasing the concentration of H2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 61 |
Go |
Q:
|
If one follows a line separating phases in a phase diagram and examines a substance at that particular pressure/temperature, which of the following can be guaranteed? |
|
A
|
At any given point, there will be 50% of one phase and 50% of another phase of the substance. |
B
|
If the line separates solid and liquid and has a negative slope, the solid is more dense than the liquid. |
C
|
All three phases exist to some degree along every point of the line. |
D
|
Along the curve which separates the gas phase from other phases, decreasing pressure will result in a predominance of gas molecules in the substance. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 62 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction is given to always be spontaneous for any temperature. Which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
Enthalpy change is negative and entropy change is negative |
B
|
Enthalpy change is negative and entropy change is positive |
C
|
Enthalpy change is positive and entropy change is negative |
D
|
Enthalpy change is positive and entropy change is positive |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 63 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following reflects the units for Kw, the ionic product for water? |
|
A
|
mol/L |
B
|
mol2/L2 |
C
|
L/mol |
D
|
L2/mol2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 64 |
Go |
Q:
|
The cell potential for a voltaic cell (E) is +1.05V. Which of the following holds true for the Gibbs free energy for this reaction? |
|
A
|
It is positive |
B
|
It is negative |
C
|
It can be either positive or negative depending on the particular redox reaction |
D
|
It equates to 0 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrochemistry | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 65 |
Go |
Q:
|
A phase diagram for a compound has a solid-liquid phase line slope is perfectly vertical. This implies that: |
|
A
|
there exist multiple temperatures for which the substance exists as both a solid and a liquid. |
B
|
a liquid phase does not exist at the same pressure/temperature parameters as the solid phase. |
C
|
no triple point exists for this compound. |
D
|
the liquid and solid phases are of the same density. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 66 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not an extensive property of a substance or system? |
|
A
|
density |
B
|
volume |
C
|
energy |
D
|
Gibbs energy |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 67 |
Go |
Q:
|
Increased temperature serves to: |
|
A
|
increase the reaction rate for a reaction. |
B
|
increase activation energy for a reaction. |
C
|
decrease activation energy for a reaction. |
D
|
maintain the same reaction rate for a reaction. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 68 |
Go |
Q:
|
As you go from left to right on a phase diagram, which of the following processes would not be seen? |
|
A
|
sublimation |
B
|
condensation |
C
|
melting |
D
|
vaporization |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 69 |
Go |
Q:
|
The specific heats in J/g·°C of iron, mercury, water, and glass are 0.44, 0.14, 4.19, and 0.84, respectively. If 5 g of each of the substances absorbs 20 J of heat, which will have the smallest temperature increase? |
|
A
|
Iron |
B
|
Mercury |
C
|
Water |
D
|
Glass |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 71 |
Go |
Q:
|
A brand of rock salt is rated down to -25 °C. The salt is indicated to be mostly composed of NaCl. Exposed to temperatures of -35 °C the salt ceases to work. If the NaCl rock salt were replaced with CaCl2 with the same molality, would the ice melt? |
|
A
|
No, because the salts are placed in the same molality. |
B
|
No, because the additional melting power of the CaCl2 would be insufficient to melt ice at -35 °C. |
C
|
Yes, because the CaCl2 would be able to melt ice down to -37.5 °C. |
D
|
Yes, because melting of CaCl2 is exothermic. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 72 |
Go |
Q:
|
In a closed system with constant temperature, pressure can be plotted against volume in a PV diagram. Given this, which of the following is NOT true? |
|
A
|
The amount of energy expended by the system can be estimated by an area on the graph. |
B
|
The relationship between pressure and volume would always be linearly decreasing. |
C
|
The change in internal energy is equal to 0. |
D
|
An appropriate example that can be plotted in this PV diagram is an ideal gas in a container (in a constant-temperature environment) which is allowed to expand slowly. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Energy & Work | Miscellaneous General Chemistry | Quantitative Skills | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 73 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction with ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0 will be: |
|
A
|
nonspontaneous. |
B
|
always spontaneous.
|
C
|
favorable at high temperatures.
|
D
|
favorable at any temperature.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Equilibrium | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 74 |
Go |
Q:
|
What information would be required to determine the specific heat of an object? |
|
A
|
The mass of the object, its volume, and the amount of heat energy it contains at a particular temperature. |
B
|
The volume of the object and its temperature at two different densities. |
C
|
The mass of the object and the amount of energy added from a starting and ending temperature. |
D
|
The density of the object and its melting and boiling points. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 75 |
Go |
Q:
|
An exergonic reaction that is endothermic should have: |
|
A
|
a low temperature and increase in entropy. |
B
|
a high temperature and decrease in entropy. |
C
|
a high temperature and increase in entropy. |
D
|
a low temperature and decrease in entropy. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 76 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction under thermodynamic control will produce: |
|
A
|
the most energetically stable product as long as the activation energy is lowest. |
B
|
the most energetically stable product regardless of the activation energy. |
C
|
the product that has the lowest activation energy regardless of the energy state of the final product. |
D
|
the product that has the lowest activation energy as long as the final product has the lowest overall energy state. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 77 |
Go |
Q:
|
An equilibrium reaction will be shifted towards the products when the temperature is increased if: |
|
A
|
the concentration of products is greater than the concentration of reactants. |
B
|
the concentration of reactants is greater than the concentration of products. |
C
|
the reaction is exothermic. |
D
|
the reaction is endothermic. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 78 |
Go |
Q:
|
Four elements, A, B, C, and D have specific heat in the following order: A>B>C>D. Which element would have the largest change in temperature when heated by a heat source? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 79 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following must hold true for a spontaneous process?
I. change in Gibbs free energy is < 0
II. change in Gibbs free energy is > 0
III. change in entropy must be > 0 |
|
A
|
I and III only |
B
|
II and III only |
C
|
I only |
D
|
II only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 80 |
Go |
Q:
|
The first law of thermodynamics states: |
|
A
|
entropy is constantly increasing. |
B
|
entropy cannot decrease in a closed system. |
C
|
the total energy of an isolated system remains constant. |
D
|
enthalpy cannot be zero for a reaction. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 81 |
Go |
Q:
|
A closed system: |
|
A
|
exchanges both mass and heat with its surroundings. |
B
|
exchanges mass but not heat with its surroundings. |
C
|
exchanges heat but not mass with its surroundings. |
D
|
exchanges neither mass nor heat with its surroundings. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 82 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following holds false regarding enthalpy? |
|
A
|
Enthalpy is considered a state function. |
B
|
The pathway that a reactant takes to become a product has no bearing on the enthalpy of this transformation. |
C
|
Change in enthalpy for a reaction is the sum of the enthalpies of formation of the products minus the sum of the enthalpies of formation of the reactants. |
D
|
In a reaction A --> B, one can calculate the enthalpy change if you only know the enthalpy of formation of product B. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 83 |
Go |
Q:
|
Reactant X can become product Y through various mechanisms. A one-step mechanism takes places with enthalpy change of A. A two step mechanism can take place where the individual reactions have enthalpies B and C, respectively. Which of the following represents the change in enthalpy from X to Y? |
|
A
|
A+B+C |
B
|
B+C-A |
C
|
B+C |
D
|
A-B-C |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 84 |
Go |
Q:
|
For a given reaction, the Gibb's free energy change at standard temperature and pressure is -7500 J/mol. Which of the following is the equilibrium constant for this reaction? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 85 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the approximate change in entropy of a system where 40,000 J of heat are used to covert 1 kg of of a liquid compound to its gaseous form at a temperature of 150 K? |
|
A
|
2.5 J/K |
B
|
25 J/K |
C
|
250 J/K |
D
|
2500 J/K |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 86 |
Go |
Q:
|
A compound has a melting point of 100 degrees Celsius. The specific heat for this compound is 2 x 103 J/mg * K. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of a kilogram of this compound from 0 degrees Celsius to 20 degrees Celsius? |
|
A
|
4 x 104 J |
B
|
4 x 106 J |
C
|
4 x 108 J |
D
|
4 x 1010 J |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 87 |
Go |
Q:
|
A liquid compound, X3 undergoes two separate reactions in a lab experiment. In reaction A, the molecule first decomposes to its elemental form (simply X, which is a solid), and then heat is applied such that the X atoms reform to create X3 gas. In reaction B, heat is applied to liquid X3 and gaseous X3 is produced. Which of the following is true for these reactions? |
|
A
|
Change in enthalpy for both reaction A and B is zero. |
B
|
Change in enthalpy is the greater for reaction A compared with reaction B. |
C
|
Change in enthalpy is the less for reaction A compared with reaction B. |
D
|
Change in enthalpy is the same and nonzero for reaction A and reaction B. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 88 |
Go |
Q:
|
In which of the following situations is a reaction never spontaneous? |
|
A
|
change in enthalpy negative and change of entropy is positive |
B
|
change in enthalpy positive and change of entropy is positive |
C
|
change in enthalpy negative and change of entropy is negative |
D
|
change in enthalpy positive and change of entropy is negative |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 89 |
Go |
Q:
|
The second law of thermodynamics makes the statement that: |
|
A
|
open systems cannot have a decrease or increase in entropy. |
B
|
total entropy cannot decrease in a closed system. |
C
|
reversible reactions have a negative change in entropy. |
D
|
energy in closed system only decreases if there is a concurrent increase in entropy. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 90 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is false regarding a phase diagram? |
|
A
|
The triple point refers to a point where solid, liquid, and gas forms all exist. |
B
|
Typically the axes on a phase diagram are temperature and pressure. |
C
|
There are regions on a phase diagram where only a single phase of a molecule is found. |
D
|
The critical point reflects the point where the solid form can no longer exist. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 91 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the change in Gibbs free energy for a reaction with a change in heat of 15,000 J and a change in entropy of 10 J/K at a temperature of 725 degrees Celcius? |
|
A
|
5000 J |
B
|
7700 J |
C
|
10000 J |
D
|
12000 J |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 92 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following holds true for an endothermic spontaneous reaction? |
|
A
|
ΔH is negative for the reaction |
B
|
the value of TΔS is positive |
C
|
the product of ΔS and ΔH is negative |
D
|
there can be no change in entropy |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 93 |
Go |
Q:
|
In a laboratory setting, a methane gas molecule is dissociated into a carbon atom and four hydrogen radicals. This process requires 1600 kJ/mol of methane. Which of the following is the bond energy of the carbon-hydrogen bond? |
|
A
|
0 kJ/mol |
B
|
400 kJ/mol |
C
|
1600 kJ/mol |
D
|
4800 kJ/mol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 94 |
Go |
Q:
|
How much energy would approximately be required to raise the temperature of 60 g of water by 20 degrees Celsius? |
|
A
|
2 kJ |
B
|
3 kJ |
C
|
4 kJ |
D
|
5 kJ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | |
|
| 95 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular substance is dissolved in water and various energy changes are measured. It is known that heat is absorbed from in this process and the equilibrium constant is measured to be less than 1. What is the sign of the standard entropy change for this process? |
|
A
|
positive |
B
|
negative |
C
|
either positive or negative |
D
|
zero |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Thermochemistry | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|