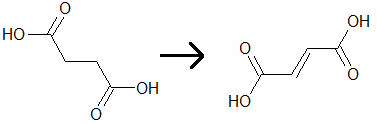|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
The cytosol is a reducing environment. Which of the following is most likely to happen to a disulfide bridge across amino acid residues in a reducing environment? |
|
A
|
Breakage of the disulfide bond with the addition of a hydrogen to each sulfur atom |
B
|
Addition of a hydrogen to each sulfur while the disulfide bridge remains intact |
C
|
Nothing |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Redox Reactions | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the combustion of methane, what is the change in oxidation state of the carbon atom from the left side of the reaction to the right and what is the reducing agent? The reaction is as follows: CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O |
|
A
|
+4 and CH4 is the reducing agent. |
B
|
+8 and O2 is the reducing agent. |
C
|
+4 and O2 is the reducing agent. |
D
|
+8 and CH4 is the reducing agent. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Certain catalysts can be used to add H2 across double-bonded carbons. Which of the following describes such a reaction?
|
|
A
|
hydration |
B
|
decarboxylation |
C
|
reduction |
D
|
oxidation |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which compound reacts with a base to form a salt and water? |
|
A
|
NaOH |
B
|
Na2CO3 |
C
|
NaCl |
D
|
CH3COOH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which half-reaction correctly represents reduction? |
|
A
|
Cr3+ + 3e- -> Cr(s) |
B
|
Cr3+ -> Cr(s) + 3e- |
C
|
Cr(s) -> Cr3+ + 3e- |
D
|
Cr(s) + 3e- -> Cr3+ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
Many mainly-nonpolar carboxylic acids with long alkyl chains are insoluble in water when protonated. With which of the following can they be reacted in order to become soluble? |
|
A
|
HCl |
B
|
NaCl |
C
|
MeOH |
D
|
NaOH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carboxylic Acids | Redox Reactions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans is an organism that oxidizes Fe2+ in FeS2 to produce sulfuric acid. What is the role of O2 in its metabolism? |
|
A
|
Electron Source |
B
|
Terminal Electron Acceptor |
C
|
Catalyst |
D
|
Reducing Agent |
|
|
|
Tags:
Oxidative Phosphorylation | Redox Reactions | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reducing agent is responsible for which of the following reactions? |
|
A
|
R-OH → R=O |
B
|
R-OH → RO2R |
C
|
R-OH → R-H |
D
|
R-OH → ROOH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the combustion of iso-octane, which of the following acts as an oxidizing agent? |
|
A
|
Water |
B
|
Carbon Dioxide |
C
|
Iso-octane |
D
|
Oxygen |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is being oxidized and reduced in the following reaction?
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
|
|
A
|
oxygen is oxidized, hydrogen is reduced |
B
|
hydrogen is oxidized, carbon is reduced |
C
|
oxygen is oxidized, carbon is reduced |
D
|
carbon is oxidized, oxygen is reduced |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which is a feature of a reducing agent? |
|
A
|
It becomes reduced |
B
|
It donates electrons to other species |
C
|
Its oxidation number decreases |
D
|
An atom with a smaller atomic radius is a better reductant |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
One of the steps of the citric acid cycle is the conversion of succinate to fumarate, which results in the reduction of FAD. This process is shown by the diagram below. Which of the following statements is(are) true regarding the reaction that occurs?
I. Fumarate will rotate polarized light differently than succinate does.
II. FAD becomes reduced to FADH2
III. The chemical potential energy of fumarate is lower than succinate.
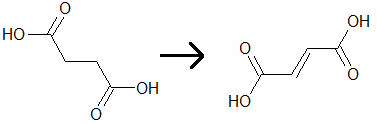 |
|
A
|
III only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Citric Acid Cycle | Atomic & Electronic Structure | Redox Reactions | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the reaction CuCl2 + 2Cl- → CuCl4-2, the CuCl2 is acting as a |
|
A
|
Bronstead-Lowry Acid |
B
|
Bronstead-Lowry Base |
C
|
Lewis Acid |
D
|
Lewis Base |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the difference in the oxidation states of selenium between SeO3-2 and SeS2? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
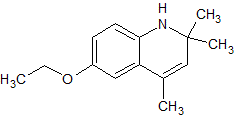
When treated with dilute acid, the compound shown below would change in which of the following ways?
|
|
A
|
Its water solubility would increase. |
B
|
It would lose the ethyl group. |
C
|
It would lose one or more double bonds. |
D
|
It would gain one or more hydroxyl groups. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the reaction Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu, which is acting as the reducing agent? |
|
A
|
Fe |
B
|
CuSO4 |
C
|
Cu |
D
|
FeSO4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
When treated with a strong oxidizing agent like CrO3, benzaldehyde will most likely produce which of the following products? |
|
A
|
benzoic acid |
B
|
phenylmethanol |
C
|
phenol |
D
|
benzene and carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
The conversion of glucose to gluconic acid is an example of which type of reaction? |
|
A
|
Acetylation |
B
|
Alkylation |
C
|
Oxidation |
D
|
Hydrogenation |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
The ion NH4+ can be described as a:
I. Bronsted-Lowry Acid
II. Arrhenius Acid
III. Lewis Acid |
|
A
|
II only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the Krebs cycle, malate and NAD+ are converted to NADH and oxaloacetate. The malate converts to oxaloacetate by having one of its alcohol groups converted into a carbonyl. From the perspective of malate, this type of reaction is an example of which of the following? |
|
A
|
reduction |
B
|
oxidation |
C
|
dehydration |
D
|
condensation |
|
|
|
Tags:
Citric Acid Cycle | Redox Reactions | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
A patina is a tarnish that covers the surface of a metal and gives it the appearance of aging. Patinas occur naturally and are common for copper. Several colors are possible for a copper patina that depend on a number of environmental factors. Marine environments, industrial environments, and arid environments all will produce a different patina. This information suggests the color is a result of which of the following? |
|
A
|
Differing temperatures resulting in different levels of copper oxidation. |
B
|
The copper adapting to its environment to produce a patina color that will best help it resist corrosion. |
C
|
Differing origins of copper mines resulting in the tendency to produce different colors when tarnishing. |
D
|
Different copper salts and oxides that form as a result of exposure to local airborne chemicals. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the following unbalanced redox reaction, which species acts as the reducing agent?
MnO4- + I- → Mn2+ + I2 |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
Hydrogenation reactions are usually also reduction reactions, whereas protonation is not reduction. The primary reason for this is: |
|
A
|
protonation only occurs with nitrogen and oxygen atoms. |
B
|
hydrogenation does not affect the oxidation state while protonation does. |
C
|
protons do not come with electrons while hydrogen atoms in hydrogenation do come with electrons. |
D
|
protons are too small to reduce compounds. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the oxidation state of the copper and sulfur in CuSO4? |
|
A
|
Cu = +2; S = +6 |
B
|
Cu = +10; S = -2 |
C
|
Cu = +5; S = +3 |
D
|
Cu = 0; S = +8 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the reaction below, which species acts as the reducing agent?
2 As (s) + 3 Cl2 (g) → 2 AsCl3 |
|
A
|
As |
B
|
Cl2 |
C
|
AsCl3 |
D
|
The reaction depicted is not a redox reaction. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
SiF4 + 2F- → SiF62-
In the reaction above, which species acts as a Lewis acid? |
|
A
|
SiF4 only |
B
|
F- only |
C
|
Both SiF4 and F- |
D
|
Neither SiF4 nor F- |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
The oxidation of hexanol to hexanoic acid would be accompanied by the appearance of which of the following peaks in an IR spectrum? |
|
A
|
1400 cm-1 |
B
|
1650 cm-1 |
C
|
2300 cm-1 |
D
|
3300 cm-1 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Electroplating involves passing a current through a solution of metal ions causing them to plate onto the surface of an object. The metal metal becomes coated on, to the object due to: |
|
A
|
Reduction of cationic metals |
B
|
Reduction of anionic metals |
C
|
Oxidation of cationic metals |
D
|
Oxidation of anionic metals |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
Treatment of certain dyes with dilute acids bleaches their color due to various oxidation reactions. If these bleached pigments are subsequently treated with dilute base, which of the following would be expected? |
|
A
|
The dye color would return because the oxidation reaction is reversible with treatment of dilute base. |
B
|
The dye color would return because the base can deprotonate the oxidized product. |
C
|
The dye color would not return because the oxidation reaction is not reversible with treatment of dilute base. |
D
|
The dye color would not return because the base can deprotonate the oxidized product. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student places metal X into a solution of MSO4 and sees a new metal coating forming over metal X. Which of the following is true regarding this scenario? |
|
A
|
Metal M is being reduced. |
B
|
Metal M is being oxidized. |
C
|
Metal M is undergoing a non-redox reaction with Metal X. |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined from the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
When Zn(s) reacts with HCl, H2g is produced because: |
|
A
|
Zinc becomes reduced in the reaction |
B
|
Zinc reduces the hydrogen ions |
C
|
H2 naturally forms whenever HCl ionizes |
D
|
Zinc and hydrogen have the same oxidation state |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
2 NH3 + OCl- → N2H4+ H2O + Cl-
Given the reaction above, which of the following is correct? |
|
A
|
Nitrogen is reduced, and OCl- is the oxidizing agent |
B
|
N2H4 is oxidized, and H2O is the reducing agent |
C
|
Chlorine is reduced, and NH3 is the reducing agent |
D
|
H2O is oxidized, and N2H4 is the oxidizing agent |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
A redox reaction proceeds with the following unbalanced equation: OH- + SO32-→SO42- + H2O. In this reaction, the oxidation state of the sulfur changes from: |
|
A
|
+2 to +4 |
B
|
+4 to +4 |
C
|
+4 to +6 |
D
|
+4 to +2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
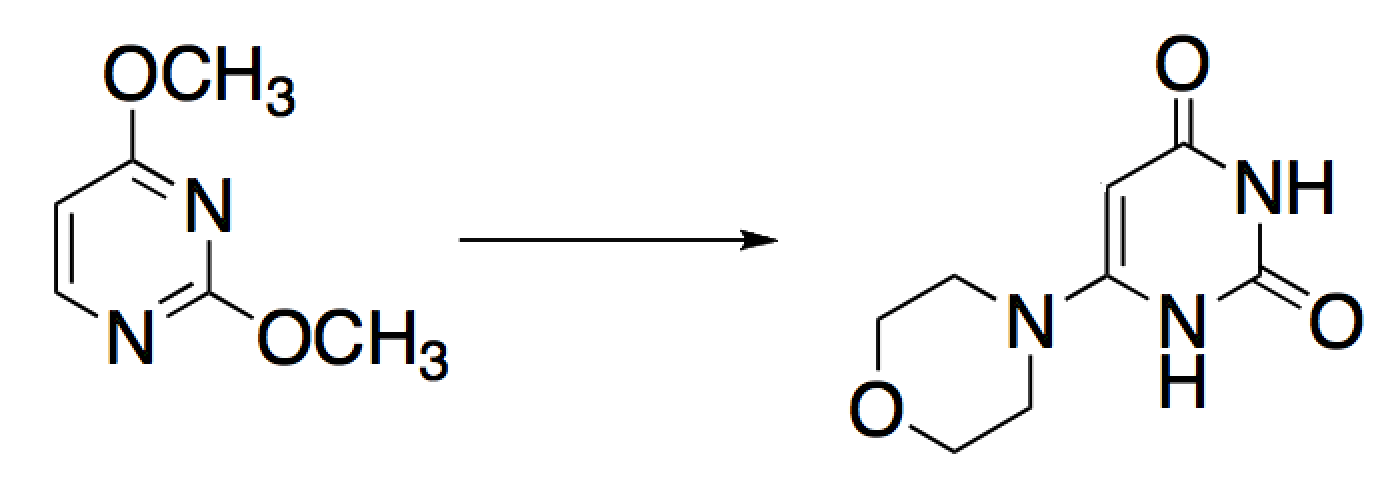
Given the reaction below, how many atoms in the aromatic ring were oxidized and how many were reduced?
|
|
A
|
0 atoms oxidized, 1 atom reduced
|
B
|
1 atom oxidized, 0 atoms reduced
|
C
|
1 atom oxidized, 1 atom reduced
|
D
|
2 atoms oxidized, 1 atom reduced
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
How does the oxidation state of carbon change when an alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde? |
|
A
|
The oxidation state increases by 2. |
B
|
The oxidation state decreases by 2. |
C
|
The oxidation state increases by 1. |
D
|
The oxidation state decreases by 1. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | Organic Chemistry Reactions | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the balance equation for the combustion of propane (C3H8), which of the following is the correct coefficient for water? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Stoichiometry | Redox Reactions | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the following reaction, what is acting as an oxidizing agent?
H2 + F2 → 2HF |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following does not depict a possible oxidative state for carbon? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following structures has the most reduced carbon atom? |
|
A
|
methanol |
B
|
methane |
C
|
carbon dioxide |
D
|
CH2O2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
For the balanced formula for the combustion of hexane, which of the following is the correct coefficient in front of oxygen gas? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
A mole of heptane undergoes a combustion reaction. How many moles of water would be expected to be produced? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction takes place where an alcohol is converted to an aldehyde. This type of reaction is referred to as a: |
|
A
|
hydrolysis reaction. |
B
|
reduction reaction. |
C
|
oxidation reaction. |
D
|
dehydration reaction. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following reactions utilizes a reducing agent? |
|
A
|
Conversion of an alcohol to an ether |
B
|
Conversion of an alcohol to an ester |
C
|
Conversion of an alcohol to a hydrocarbon |
D
|
Conversion of an alcohol to a carboxylic acid |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
An alkyl halide is formed with various halide R-groups. Which of the following R-groups would yield the molecule with the least likelihood of participating in an SN2 reaction? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|