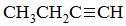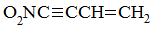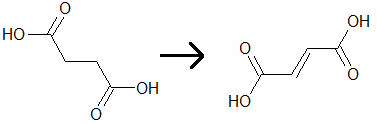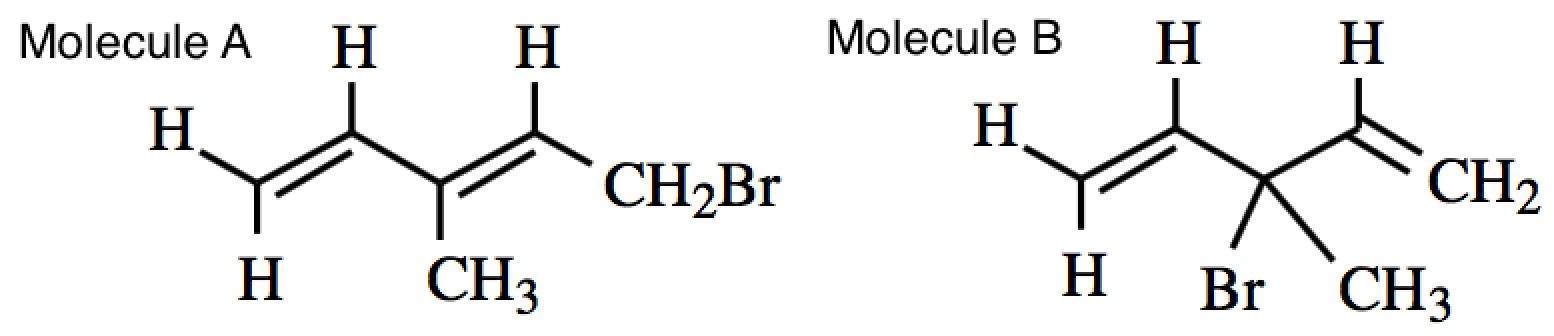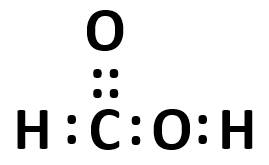|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
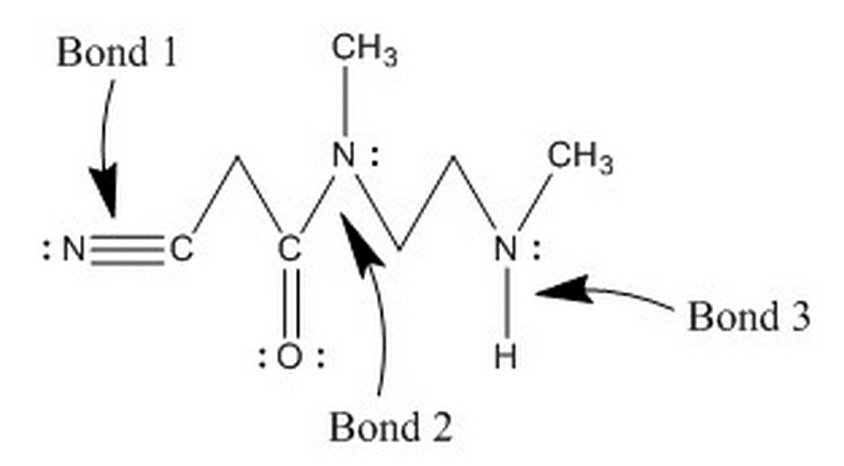
The cytosol is a reducing environment. Which of the following is most likely to happen to a disulfide bridge across amino acid residues in a reducing environment? |
|
A
|
Breakage of the disulfide bond with the addition of a hydrogen to each sulfur atom |
B
|
Addition of a hydrogen to each sulfur while the disulfide bridge remains intact |
C
|
Nothing |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Redox Reactions | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds is expected to have the lowest vapor pressure? |
|
A
|
CH3OCH3 |
B
|
CH3CH2OH |
C
|
CH3CH2CH3 |
D
|
CH3Cl |
|
|
|
Tags:
Alcohols | Gases | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the major intermolecular force of the following compound?
 |
|
A
|
dipole-dipole |
B
|
hydrogen bonding |
C
|
London dispersion |
D
|
ionic |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the major intermolecular force in the following compound?
(CH3CH2)3N |
|
A
|
dipole-dipole |
B
|
hydrogen bonding |
C
|
London dispersion |
D
|
ionic |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules does not contain at least one glycosidic bond? |
|
A
|
Sucrose |
B
|
Maltose |
C
|
Glycogen |
D
|
Ribose |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
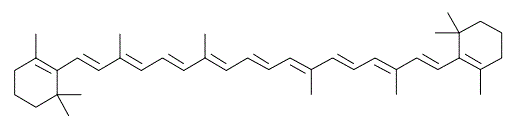
Alternating double and single bonds, including in hydrocarbons, results in electron delocalization. Absorption wavelength is directly proportional to the quantity of delocalized electrons. Which of the following compounds would be expected to absorb at the highest wavelength? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not an example of a conjugated system? |
|
A
|
1,3-butadiene |
B
|
benzene |
C
|
cyclobutadiene |
D
|
1,2-butadiene |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Phosphorus had 3 allotropes: red, white, and black.
White is most reactive due in large part to having 60
degree bonds in a tetrahedral formation. Which of the
following best explains the reason for the bond angle
increasing reactivity? |
|
A
|
60 degree angles are energetically favorable, making
the allotrope less stable and thus more reactive. |
B
|
60 degree angles are energetically unfavorable, making
the allotrope less stable and thus more reactive. |
C
|
60 degree angles are energetically favorable, making
the allotrope more stable and thus more reactive. |
D
|
60 degree angles are energetically unfavorable, making
the allotrope more stable and thus more reactive. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following alkenes is the most stable? |
|
A
|
ethylene |
B
|
prop-1-ene |
C
|
2,3 methyl but-2-ene |
D
|
trans but-2-ene |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
One of the steps of the citric acid cycle is the conversion of succinate to fumarate, which results in the reduction of FAD. This process is shown by the diagram below. Which of the following statements is(are) true regarding the reaction that occurs?
I. Fumarate will rotate polarized light differently than succinate does.
II. FAD becomes reduced to FADH2
III. The chemical potential energy of fumarate is lower than succinate.
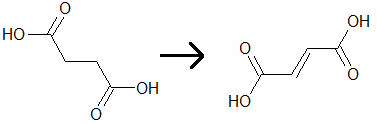 |
|
A
|
III only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Citric Acid Cycle | Atomic & Electronic Structure | Redox Reactions | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following reactions produces a double bond from two sp3-hybridized carbon atoms, as in the diagram below?
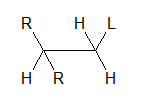
I. SN1
II. SN2
III. E1 |
|
A
|
III only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
I and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following does not have a dipole moment? |
|
A
|
trans-1,2-dichloroethane |
B
|
cis-1,2-dibromoethane |
C
|
ammonia |
D
|
chloroform (CHCl3) |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Comparing cis-1,2-dibromoethene to trans-1,2-dibromoethene, which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
trans-1,2-dibromoethene has a dipole moment while cis-1,2-dibromoethene does not |
B
|
trans-1,2-dibromoethene experiences more steric hindrance than cis-1,2-dibromoethene |
C
|
cis-1,2-dibromoethene has a higher boiling point than trans-1,2-dibromoethene |
D
|
both compounds have identical physical and chemical properties |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
A chlorine atom can form
I. A single sigma bond
II. Four sigma bonds and three pi bonds
III. Four sigma bonds and four pi bonds |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following does not differ between ethene and ethyne? |
|
A
|
the number of pi bonds between the carbon atoms |
B
|
the number of sigma bonds between the carbon atoms |
C
|
boiling point |
D
|
molecular weight |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following alkyl halides would most likely undergo an SN2 reaction? |
|
A
|
CH3CH2Cl |
B
|
CH3CH2F |
C
|
CH3CH2I |
D
|
CH3CH2Br |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
A carbonyl carbon acts an electrophile because |
|
A
|
the difference in electronegativity between oxygen and carbon is enough to polarize the bond |
B
|
it has sp2 hybridization |
C
|
oxygen can donate electron density to stabilize the positively-charged electrophile |
D
|
all carbon atoms act as electrophiles |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Table | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
Infrared spectroscopy relies in the absorption of light by bonds in which there is a permanent dipole. Which of the following molecules would have the weakest absorbance of infrared light? |
|
A
|
Cl-Cl |
B
|
C=O |
C
|
C-H |
D
|
O-H |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
Dipole moments are measured in units of D where the larger the number, the stronger the dipole. If the dipole moment for a CH bond is 1.57 and an NH bond is 1.63, which of the following would be the dipole moment observed for an OH bond? |
|
A
|
0.24 |
B
|
1.53 |
C
|
1.78 |
D
|
9.21 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
Disulfide bonds are extremely important in protein folding and a number of other physiologic interactions. Which of the following would be capable of destroying such a disulfide bond? |
|
A
|
Reducing agent |
B
|
Oxidizing agent |
C
|
Chelating agent |
D
|
All of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
Protein-protein interactions are usually reversible and temporary. These interactions are mediated by a number of different mechanisms. Which of the following is NOT found in such temporary protein-protein interactions?
I. Hydrophobic interactions
II. Ionic bonds
III. Covalent bonds |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
III only |
C
|
I and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Both nucleophilic substitution and addition deal with the attack of a nucleophile onto an electrophile. The primary difference between the two, however, is that |
|
A
|
nucleophilic addition involves a good leaving group while nucleophilic substitution does not. |
B
|
nucleophilic addition can follow either SN1 or SN2 mechanisms while nucleophilic substitutions can only follow SN1 mechanisms. |
C
|
nucleophilic substitution and addition are competing mechanisms for the same reaction. |
D
|
nucleophilic addition involves the replacement of a π bond with two new σ bonds while nucleophilic substitution primarily occurs with the replacement of existing σ bonds. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Compared to a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group would be expected to: |
|
A
|
be smaller in size. |
B
|
increase the strength of an acid on the alpha carbon. |
C
|
have less steric hindrance. |
D
|
donate electron density to the alpha carbon. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the LEAST effective chlorinating agent? |
|
A
|
SOCl2 |
B
|
PCl3 |
C
|
HCl |
D
|
CCl4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
The transformation of 2-methylbutene to 2-ethylbutane requires a transformation from |
|
A
|
An sp orbital to an sp3 orbital |
B
|
An sp3 orbital to an sp2 orbital |
C
|
An sp2 orbital to an sp3 orbital |
D
|
An sp3 orbital to an sp orbital |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
The lone pairs on the oxygen atom in H2O allow it to act as which of the following when accepting a proton to form H3O+? |
|
A
|
Lewis base |
B
|
Lewis acid |
C
|
Arrhenius base |
D
|
Arrhenius acid |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds would be expected to have the least amount of steric strain on its bonds? |
|
A
|
cyclopropane |
B
|
cyclobutane |
C
|
cyclopentane |
D
|
cyclohexane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
What are the formal charges on each atom, respectively, in the following molecule: O-N≡O |
|
A
|
-1, 0, +1 |
B
|
-1, +1, +1 |
C
|
+1, +1, -1 |
D
|
0, +1, -1 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
Certain insoluble organic compounds can often be rendered water-soluble in the presence of an acid or a base. Such organic compounds become water soluble because of which of the following? |
|
A
|
The organic compound becomes ionic. |
B
|
The organic compound reacts to remove hydrophobic groups. |
C
|
The organic compound reacts to form water-soluble carboxyl groups. |
D
|
The acid or base increase the polarity of the water and make it easier for the compound to dissolve. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following bonds would be expected to be the most polar? |
|
A
|
H-O |
B
|
H-S |
C
|
H-Se |
D
|
H-Te |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the orbital hybridization of XeF4? |
|
A
|
sp3 |
B
|
sp4 |
C
|
sp3d |
D
|
sp3d2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the reaction between BH3 and N(CH3)3 to form BH3N(CH3)3, the N(CH3)3 acts as which of the following? |
|
A
|
Lewis acid |
B
|
Lewis base |
C
|
Bronsted-Lowry acid |
D
|
Bronsted-Lowry base |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
Formaldehyde is considered the most simple carbonyl molecule, with a C=O bond and two hydrogen atoms bound to carbon. For the oxygen, which orbitals have become hybridized (by VSEPR theory) to be in such a bond with carbon? |
|
A
|
one 2s and one 2p orbital |
B
|
one 2s and two 2p orbitals |
C
|
two 2s and two 2p orbitals |
D
|
No orbitals are hybridized in the structure |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the formal charge of the single-bonded oxygen in NO2-? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding a molecule with sp3 hybridized orbitals? |
|
A
|
Its structure is always tetrahedral |
B
|
Its structure is always trigonal planar |
C
|
The angles between the groups will consistently be 109.5 degrees |
D
|
Its structure is determined by the groups bound to the central atom |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following orbitals can participate in sigma bonds?
I. s-oribtals
II. p-oribtals
III. d-oribtals |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
The formal charge on each atom of ozone (O3) is |
|
A
|
0 |
B
|
-1, +1, +1 |
C
|
-1, 0, +1 |
D
|
-1, 0 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 51 |
Go |
Q:
|
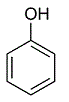
Given the structure below, the hybridization, electronic geometry, and observable geometry of the oxygen atom is:
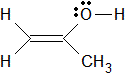
|
|
A
|
sp2, trigonal planar, trigonal planar |
B
|
sp2, trigonal planar, bent |
C
|
sp3, tetrahedral, tetrahedral |
D
|
sp3, tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is created when an electron pair is shared between two atoms of EQUAL electronegativity? |
|
A
|
Polar covalent bond |
B
|
Nonpolar covalent bond |
C
|
Ionic bond |
D
|
Electron transfer |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, which of the following best describes the dipole moment?
 |
|
A
|
Dipole moment present, points toward sulfur
|
B
|
Dipole moment present, points toward the chlorines
|
C
|
Dipole moment present, points toward the carbons
|
D
|
No dipole moment present
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best describes the type of bond formed when sodium and chlorine react? |
|
A
|
Dispersion bond
|
B
|
Ionic bond |
C
|
Polar covalent bond
|
D
|
Nonpolar covalent bond
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Table | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 56 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following correctly describes a polar covalent bond? |
|
A
|
Involves a transfer of electrons to the atom of less electronegativity
|
B
|
Involves equal sharing of an electron pair between two atoms
|
C
|
Involves unequal sharing of an electron pair between two atoms
|
D
|
Results in the formation of oppositely charged ions
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the connectivity below, which of the following classifications/descriptions do NOT apply to the two isomers possible due to the carbon bonded to the bromine?
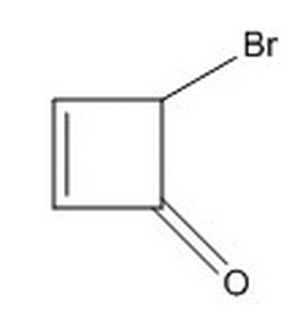 |
|
A
|
Enantiomers |
B
|
Diastereomers |
C
|
Stereoisomers |
D
|
Both molecules are optically active
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 60 |
Go |
Q:
|
Carboxyl groups have higher boiling points than acid halides because they are capable of self-associating with hydrogen bonds to form dimeric associations. Acid halides, however, are only capable of receiving hydrogen bonds, not donating them, and cannot self-associate with hydrogen bonds. The structure on acid halides and carboxylic acids that receives hydrogen bonds is the: |
|
A
|
carbon of the carbonyl group |
B
|
oxygen of the carbonyl group |
C
|
oxygen of the hydroxyl group |
D
|
carbon of the R-group |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Carboxylic Acids | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 61 |
Go |
Q:
|
An allylic substitution reaction results in two regioisomeric monobromides, as shown below. Which of the following statements about their relative stabilities is correct?
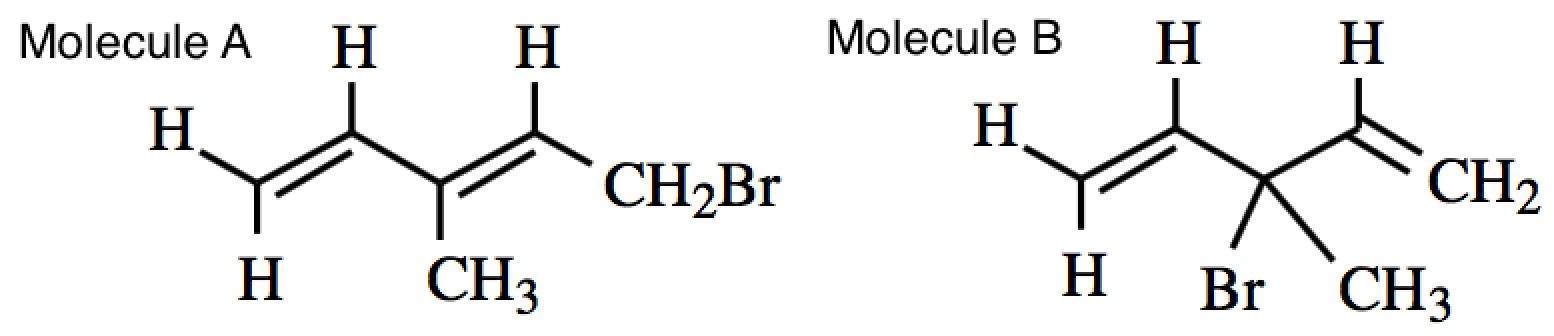 |
|
A
|
Molecule A is more stable because it has a more sterically hindered bromine.
|
B
|
Molecule A is more stable because it has conjugated double bonds.
|
C
|
Molecule B is more stable because it has a less sterically hindered bromine.
|
D
|
Molecule B is more stable because it has conjugated double bonds.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | Organic Chemistry Reactions | |
|
| 62 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following will increase the vapor pressure of a liquid? |
|
A
|
Decreasing the temperature of the liquid
|
B
|
Increasing the temperature of the liquid
|
C
|
Decreasing the surface area of the liquid
|
D
|
Increasing the surface area of the liquid
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Fluids | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 63 |
Go |
Q:
|
For the molecule arsenic pentachloride (AsCl5), which of the following correctly depicts the hybridization of the arsenic atom? |
|
A
|
sp2 |
B
|
sp3 |
C
|
sp3d |
D
|
sp3d2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 64 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT a type of internal energy? |
|
A
|
rotational |
B
|
translational |
C
|
refractory |
D
|
vibrational |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 65 |
Go |
Q:
|
What percentage 's' character do the orbitals of methane possess? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 66 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following correctly lists the combination of orbitals required to form a triple bond? |
|
A
|
3 sigma bonds |
B
|
3 pi bonds |
C
|
2 sigma bonds, 1 pi bond |
D
|
1 sigma bond, 2 pi bonds |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 67 |
Go |
Q:
|
The formal charges on each atom of carbon dioxide are: |
|
A
|
0, 0, and 0. |
B
|
0, 0, and 2. |
C
|
0, 2, and 2. |
D
|
2, 2, and 2. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 68 |
Go |
Q:
|
Benzoic acid is composed of a benzene molecule with a carboxyl group attached. Assuming that the carboxyl group is at the 1- position, an R group is added to the 4- position, which of the following R groups would result in the highest pKa of the carboxyl group? |
|
A
|
-CF3 |
B
|
-NH3+ |
C
|
-COOH |
D
|
-CH3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 69 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the oxidation of vanadium (V) in the vanadate ion (VO43-)? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 70 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules does not include a polar covalent bond? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 71 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ethene and ethyne differ in terms of:
I. boiling point
II. the number of sigma bonds between the carbons
III. the number of pi bonds between the carbons |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
I only |
D
|
I, II and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 72 |
Go |
Q:
|
In a laboratory setting, a methane gas molecule is dissociated into a carbon atom and four hydrogen radicals. This process requires 1600 kJ/mol of methane. Which of the following is the bond energy of the carbon-hydrogen bond? |
|
A
|
0 kJ/mol |
B
|
400 kJ/mol |
C
|
1600 kJ/mol |
D
|
4800 kJ/mol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 73 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following bond types lend themselves to free rotation?
I. single bond
II. double bond
III. triple bond |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 74 |
Go |
Q:
|
What types of bonds exist between the carbon and other atoms seen below?
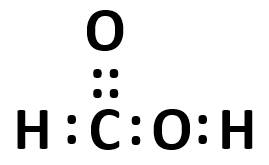 |
|
A
|
4 sigma bonds |
B
|
2 sigma bonds and 2 pi bonds |
C
|
3 sigma bonds and 1 pi bond |
D
|
8 sigma bonds |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 75 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following types of bonds can be broken by a physical reaction? |
|
A
|
Peptide bonds |
B
|
Covalent bonds |
C
|
Intramolecular bonds |
D
|
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|