|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
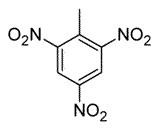
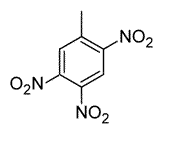
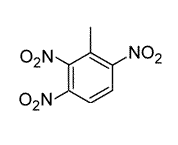
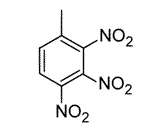
Toluene is treated with excess concentrated nitric acid, HNO3. Given that CH3 is an ortho/para director, which of the following best describes the product of the reaction? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the compound below, the two groups with the double-bonded oxygen atoms are which functional group?
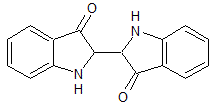 |
|
A
|
carboxyl |
B
|
carbonyl |
C
|
ester |
D
|
ether |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
A double replacement reaction occurs in a beaker between reagent X and reagent Y. It is found that water is formed in the reaction. Which of the following cannot be a potential reagent in the reaction? |
|
A
|
HCl |
B
|
NaOH |
C
|
MgCl2 |
D
|
All of the above are potential reagents |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
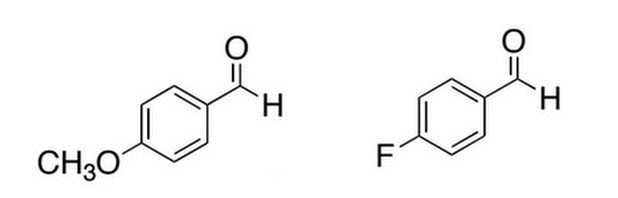
Given the two benzaldehyde derivatives below, which one will react faster (at the carbonyl carbon) with a nucleophile?
 |
|
A
|
The left molecule because the fluoro group is electron-withdrawing, making its carbonyl carbon less electrophilic for addition by a nucleophile
|
B
|
The left molecule because the fluoro group is electron-donating, making its carbonyl carbon less electrophilic for addition by a nucleophile
|
C
|
The right molecule because the fluoro group is electron-withdrawing, making its carbonyl carbon more electrophilic for addition by a nucleophile
|
D
|
The right molecule because the fluoro group is electron-donating, making its carbonyl carbon more electrophilic for addition by a nucleophile
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Aldehydes and Ketones | Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
The nitrogen-containing reactant below (Reactant B) can act as a nucleophile in certain reactions. The reaction below is carried out in a pH = 4.5 buffer. This is because the pKa of the protonated carbonyl (Reactant A) is between -2 and -8, so there is a low concentration of this highly reactive electrophile at a pH of 4.5. If the pH is further lowered (from 4.5) in order to try and increase the concentration of this electrophile, which of the following correctly describes the likely counter-effect?
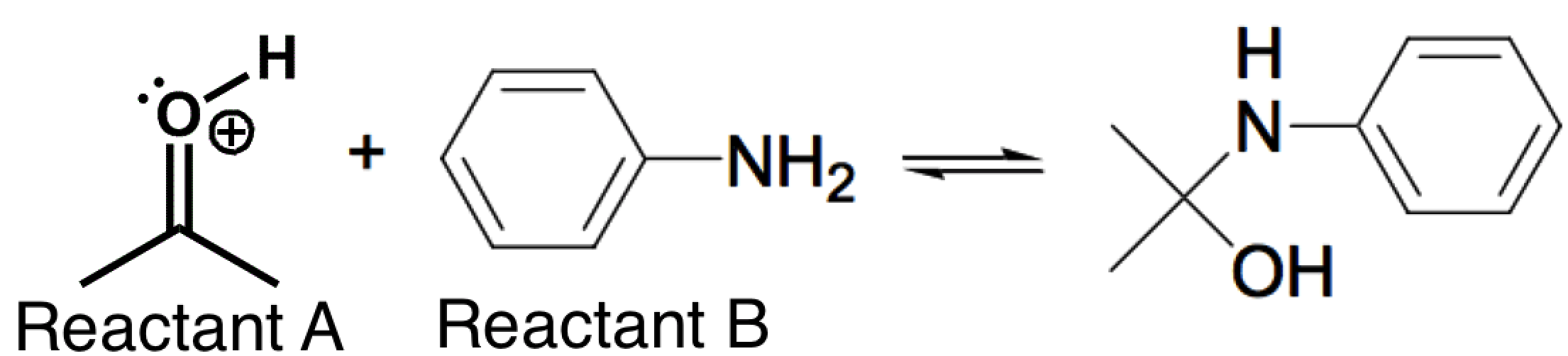 |
|
A
|
Increasing the acidity would cause less of Reactant B to become protonated (decreasing its nucleophilicity), and this would counteract the increase in electrophilicity of Reactant A.
|
B
|
Increasing the acidity would cause more of Reactant B to become protonated (decreasing its nucleophilicity), and this would counteract the increase in electrophilicity of Reactant A.
|
C
|
Increasing the acidity would cause more of Reactant B to become protonated and this would have no effect on the electrophilicity of Reactant A.
|
D
|
Increasing the acidity would have no effect on Reactant B and no effect on the electrophilicity of Reactant A.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | Organic Chemistry Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
A nucleophilic reaction to a carbonyl is considered neither an SN1 nor SN2 reaction because: |
|
A
|
no substitution occurs during nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl. |
B
|
the reaction proceeds through an E1 or E2 mechanism instead. |
C
|
the solvent for the reaction is not aqueous. |
D
|
the solvent for the reaction is not polar. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | Organic Chemistry Reactions | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
With respect to IR spectroscopy, a hydroxyl group typically contributes a:
I. narrow peak.
II. broad peak.
III. peak around 3300 cm-1.
IV. peak around 1600 cm-1. |
|
A
|
I and III |
B
|
I and IV |
C
|
II and III |
D
|
II and IV |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Meso compounds: |
|
A
|
do not contain stereocenters. |
B
|
always contain at least one double bond. |
C
|
may only contain a single chiral center. |
D
|
never have optical activity. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
The R enantiomer of a compound rotates light -8 degrees. A solution composed of 90% S enantiomer and 10% enantiomer would rotate light: |
|
A
|
-5.8 degrees. |
B
|
-6.4 degrees. |
C
|
6.4 degrees. |
D
|
5.8 degrees. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following laboratory techniques would allow for separation of enantiomers? |
|
A
|
distillation |
B
|
chiral chromatography |
C
|
electrophoresis |
D
|
affinity chromatography |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
A molecule is found to contain a S stereocenter. This implies: |
|
A
|
the molecule rotates light clockwise. |
B
|
the molecule rotates light counterclockwise. |
C
|
the molecule rotates light but the direction is unknown from this data. |
D
|
nothing about the molecule's ability to rotate light. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
cis-1,2-difluoroethene is also known as: |
|
A
|
(E)-1,2-difluoroethene. |
B
|
(Z)-1,2-difluoroethene. |
C
|
(R)-1,2-difluoroethene. |
D
|
(S)-1,2-difluoroethene. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following reaction types is least likely for a tertiary alkyl halide? |
|
A
|
SN1 |
B
|
SN2 |
C
|
E1 |
D
|
All of the above are equally unlikely |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|