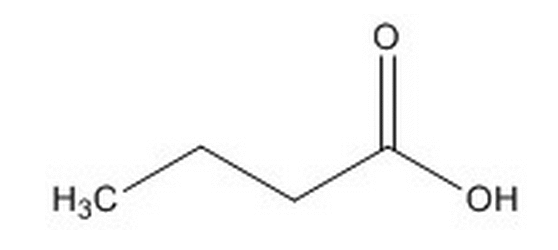
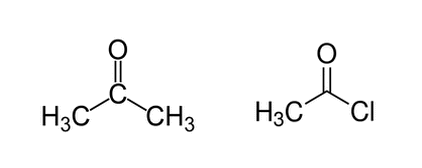
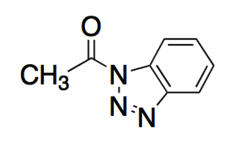
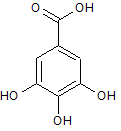
Go to Random Question
| 1 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 2 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 3 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 4 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 5 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 6 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 7 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 8 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 9 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 10 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||
| 11 | Go |
|
|||||||||||||||