|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
During vacuum distillation, what is the purpose of decreasing the pressure? |
|
A
|
to increase the boiling point |
B
|
to decrease the boiling point |
C
|
to slow down the distillation |
D
|
to stop the distillation once completed |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
After a chemical extraction you are unsure about whether you have any chloride ions in your solution. Which is the best option for testing the presence of chloride in your solution?
|
|
A
|
Sodium Nitrate |
B
|
Silver Nitrate |
C
|
Iron Sulfate |
D
|
Ammonium Sulfate |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Separation and Purification | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
During fractional distillation, hydrocarbons are separated according to their |
|
A
|
boiling points |
B
|
melting points |
C
|
triple points |
D
|
saturation points |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
During fractional distillation, hydrocarbons are separated according to their |
|
A
|
boiling points |
B
|
melting points |
C
|
triple points |
D
|
saturation points |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
Three identical solutions are brought to their cloud point.
Solution 1 is kept at its cloud point and solute is added
Solution 2 is heated above its cloud point
Solution 3 is cooled below its cloud point
If each solution is filtered, which would you expect will have precipitate remain in the filter? |
|
A
|
Solution 1 and 2 |
B
|
Solution 2 only |
C
|
Solution 1 and 3 |
D
|
Solution 3 only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Separation and Purification | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
An azeotrope is a mixture of two or more liquids which distill together as if they were a single compound. Ethanol and water form an azeotrope, making it difficult to purify ethanol. Addition of benzene can help to solve this problem: benzene, ethanol, and water boil at a ratio of 7:17:76 water:ethanol:benzene. This leaves behind almost all of the excess ethanol. During a distillation, you work with a mixture whose ratio is 7:20:76. What remains after the water:ethanol:benzene azeotrope has boiled off? |
|
A
|
3 parts ethanol |
B
|
Everything; the azeotrope will not boil if the liquids are not in the correct proportions. |
C
|
Nothing; the azeotrope will adjust to accommodate the extra 3 parts of ethanol |
D
|
This this cannot be determined based on the starting ratios because adjustments to the starting proportions can have unpredictable consequences on the ratio at which the azeotrope will boil. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following pairs of analytes cannot be separated using liquid chromatography with
water as the mobile phase and a cationic stationary phase? |
|
A
|
a tertiary amine and a carboxylic acid |
B
|
an alcohol and a carboxylic acid |
C
|
D-glucose and L-glucose |
D
|
All of the pairs of analytes can be separated in this manner |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
In thin-layer chromatography using a cellulose matrix, a mobile phase with a 1:9 ratio of ethyl acetate : petroleum ether is used on the compound shown below. If a solvent ratio of 3:7 ethyl acetate : petroleum ether were used instead, what would happen to the Rf value of the compound?
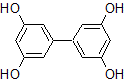 |
|
A
|
It would increase, because the polarity of the mobile phase is increasing |
B
|
It would increase, because the polarity of the mobile phase is decreasing |
C
|
It would decrease, because the polarity of the mobile phase is increasing |
D
|
It would decrease, because the polarity of the mobile phase is decreasing |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student has crystallized a compound and is concerned there may be an impurity. The presence of the impurity can be most easily determined by which of the following techniques? |
|
A
|
fractional distillation |
B
|
rotary evaporation |
C
|
melting point analysis |
D
|
thin layer chromatography |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds would be expected to travel farthest in a paper chromatography separation experiment? |
|
A
|
1-propanol |
B
|
hexane |
C
|
acetone |
D
|
methanol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ca2+ ions can be readily sequestered from solution by precipitation with ions such as carbonate. Sodium, however, is difficult to sequester because sodium: |
|
A
|
is a smaller ion. |
B
|
has a lower ionic charge. |
C
|
is more reactive than calcium. |
D
|
has few insoluble salts. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
How much mass will be left over if 100 g of CuSO4•5H2O are dried at 250 °C for 2 hours? |
|
A
|
35 g |
B
|
65 g |
C
|
85 g |
D
|
100 g |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following pairs of molecules would be most easily separated by liquid chromatography with a nonpolar stationary phase and a polar mobile phase? |
|
A
|
D-alanine and L-alanine |
B
|
2-propanol and 1-propanol |
C
|
free fatty acid and phospholipid |
D
|
D-glucose and L-glucose |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
Treatment of methane with Cl2 at 450 °C produces a mixture of chlorinated products including CH3Cl, CH2Cl2, CHCl3, and CCl4. Distillation is an effective technique for separating the products because: |
|
A
|
the products are all miscible with each other |
B
|
the boiling points of the products are distinct and sufficiently different from each other to be separated |
C
|
the products are all similar in size and can be isolated together |
D
|
the products all boil at or below room temperature |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student prepares a solution of ethanol and adds one equivalent of PBr3 to the mixture. The student extracts the alkyl product and then adds an equivalent of CH3Li to the purified product in solution. What is the final product of the reactions?
|
|
A
|
Propane |
B
|
1-Bromoethanol |
C
|
1-bromo-2-propanol |
D
|
2-propanol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Separation and Purification | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student plans on performing a liquid-liquid extraction to isolate an analyte from aqueous solution into acetone. Which of the following will most likely result from this experimental setup? |
|
A
|
The extraction will work because organic solvents are not miscible with water. |
B
|
The extraction will work because solvent choice is not relevant to liquid-liquid extraction efficiency. |
C
|
The extraction will not work because the analyte is not soluble in acetone. |
D
|
The extraction will not work because the solvents are miscible |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
During the purification of citric acid, the ferment is treated with lime which precipitates the citric acid in the form of calcium citrate. The precipitate can then be reverted back to citric acid by treating it with which of the following? |
|
A
|
H2SO4 |
B
|
NaOH |
C
|
NH4OH |
D
|
CaCl2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
Three solutions are mixed, each with a high concentration of amino acids. Solution A has a high concentration of basic amino acids, Solution B has a high concentration of acidic amino acids, and Solution C is nearly all non-polar amino acids. Using isoelectric focusing as an electrophoresis method to distinguish these proteins, and given that the bottom of the gel is toward a lower pH, which of the following lists (from bottom to top) the positions of these proteins as a result of the separation? |
|
A
|
Basic proteins, non-polar proteins, acidic proteins
|
B
|
Non-polar proteins, acidic proteins, basic proteins
|
C
|
Acidic proteins, basic proteins, non-polar proteins
|
D
|
Acidic proteins, non-polar proteins, basic proteins
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Separation and Purification | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
A step in the lab procedure for a protein analysis involves placing cytoplasmic protein in a hydrocarbon (e.g. hexane). Which of the following would most likely NOT happen next? |
|
A
|
The protein would fold itself into a different conformation
|
B
|
The protein would retain the conformation it had prior to entering the hydrocarbon solution
|
C
|
The polar side-groups would orient themselves away from hydrocarbon
|
D
|
The nonpolar side-groups would interact with the hydrocarbon molecules via Van der Waals interactions
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Separation and Purification | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following techniques is used to separate cellular proteins and is characterized by proteins leaving the mobile phase and associating with a negatively charged immobile substrate? |
|
A
|
Cation exchange chromatography
|
B
|
Anion exchange chromatography
|
C
|
Affinity chromatography
|
D
|
Micellar liquid chromatography
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | Protein Structure and Function | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following would NOT effectively separate amino acids and fatty acids? |
|
A
|
Separating on the basis of the properties (charge and binding affinities) of amino groups.
|
B
|
Separating based on the reactivity of any carboxylic acid group present.
|
C
|
Separating in water on the basis of solubility differences.
|
D
|
Separating the two based on the difference in size and shape.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | Separation and Purification | Protein Structure and Function | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
Four compounds undergo paper chromatography with an Rf distribution as follows: D>C>B>A. Which of the following is the most polar molecule? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Separation and Purification | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|

