|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
A solution of unknown acid is titrated with NaOH and the following titration curve is seen.
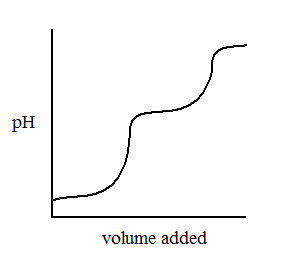
What is the most likely identity of the acid? |
|
A
|
HCl |
B
|
H2O |
C
|
H2SO4 |
D
|
H3PO4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
A titration was performed on a weak acid of pKa 5 with an extremely strong base. On the titration curve, at which pH will the equivalence point be seen?
|
|
A
|
Less than 7 |
B
|
7 |
C
|
Greater than 7 |
D
|
Not enough information given |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
The pKa of the amino acid tyrosine is between 10.0 and 10.3. Tyrosine molecule R groups are phenolics, with the hydroxyl hydrogen titrating in the pH range given. If a given solution of tyrosine molecules is brought from pH 9 to pH 11, what do you expect to occur to the hydroxyl group? |
|
A
|
The hydroxyl will go from being protonated at pH 9 to being deprotonated at pH 11 |
B
|
The hydroxyl will go from being deprotonated at pH 9 to being protonated at pH 11 |
C
|
The hydroxyl will remain deprotonated during the pH shift |
D
|
The hydroxyl will remain protonated during the pH shift |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
A weak acid is titrated with NaOH. The equivalence point will occur at a pH |
|
A
|
Less than 7 |
B
|
of 7 |
C
|
Greater than 7 |
D
|
dependent on the pKa of the weak acid |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
A buffer is made for an experiment to a pH of 7.5. The scientist realizes that the volume of the buffer is 5 mL too low, and adds 5 mL of water. What will be the pH of the subsequent solution? |
|
A
|
pH < 7 |
B
|
7 < pH < 7.5 |
C
|
pH = 7.5 |
D
|
pH > 7.5 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
At which pH could the equivalence point of a weak base titrated with hydrochloric acid be reached? |
|
A
|
5.6 |
B
|
7 |
C
|
7.5 |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
0.045 moles of NaOH are used to titrate 500 mL of a 0.030 M solution of an acid. What is the most likely identity of the acid? |
|
A
|
HCl |
B
|
H2SO4 |
C
|
H3PO4 |
D
|
Cannot be determined based on the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
A titration was performed on a weak acid of pKa 6 with an extremely strong base. On the titration curve, at which pH will the equivalence point be seen? |
|
A
|
Less than 7 |
B
|
7 |
C
|
Greater than 7 |
D
|
Not enough information given |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
Oxalic acid, H2C2O4, is a diprotic acid with a pKa value of 1.19. If 0.10 M oxalic acid is titrated 0.10 M NaOH, what would be the pH halfway to the first equivalence point? Relevant equilibria are given below:
H2C2O4 + H2O ↔ H3O+ + HC2O4- (pKa1 = 1.19)
HC2O4- + H2O ↔ H3O+ + C2O4-2 (pKa2 = 4.21) |
|
A
|
1.19 |
B
|
4.21 |
C
|
2.70 |
D
|
2.11 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Titrations | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
What volume of a 0.4 M solution of NaOH is necessary to take the pH of a 36 ml solution of 0.8 M HCl to 7.0? |
|
A
|
18 mL |
B
|
32 mL |
C
|
36 mL |
D
|
72 mL |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Titrations | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
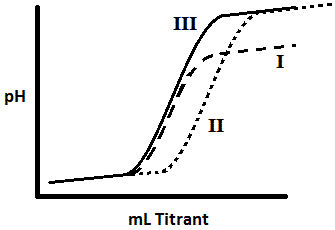
The graph above is a titration curve of three different solutions. Solution I is titrated with a base of a lower pH. Rank the solutions in terms of the strength of the acid in the solution. |
|
A
|
I < II < III |
B
|
III < I < II |
C
|
II < III < I |
D
|
There is no difference among the strength of the acids. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Arginine has a pKa of 12.48. At which pH will >50% of the R-groups in a solution of arginine be positively charged? |
|
A
|
13.58 |
B
|
12.48 |
C
|
11.09 |
D
|
Cannot be determined from the information given |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Solid NaOH is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air. A student places solid NaOH into a weighing dish and leaves the sample out for too long before weighing it. The student then dissolves the NaOH and uses the solution in a titration of an acid. The measured amount of the acid will therefore be |
|
A
|
less than the actual amount of acid |
B
|
greater than the actual amount of acid |
C
|
equal to the actual amount of acid |
D
|
the answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
A weak base is titrated with H2SO4. The equivalence point will occur at a pH that is: |
|
A
|
Less than 7 |
B
|
Exactly 7 |
C
|
Greater than 7 |
D
|
Dependent on the pKb of the base |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Titrations | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
An acid, HX, has an acid dissociation constant of 7*10-3. Which of the following is the expected pH of a solution that contains equal concentrations of HX and X- (the conjugate base of HX)? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
An acid is titrated with a sodium hydroxide and a titration curve is developed. The half-equivalence point is found to be at a pH of approximately 4 and the equivalence point is found to be at a pH of approximately 8. What is the Ka of this acid? |
|
A
|
10-3 |
B
|
9 x 10-5 |
C
|
1.2 x 10-8 |
D
|
9 x 10-10 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
If 0.025 L of a 4M solution of sodium hydroxide is titrated with hydrochloric acid, how many millimoles of hydrochloric acid would be expected to be used in the reaction? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
A titration curve is developed from an unknown acid and it is found that there are two equivalence points. Which of the following acids would be a possible identity of the unknown acid? |
|
A
|
HSO4- |
B
|
H2SO4 |
C
|
H3PO4 |
D
|
H4P2O7 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
65 mL of 9 M sodium hydroxide is added in a titration reaction with hydrochloric acid. Approximately how many mmol of HCl would be utilized in this reaction? |
|
A
|
0.6 mmol |
B
|
6 mmol |
C
|
60 mmol |
D
|
600 mmol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Titrations | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|


