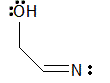
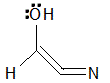
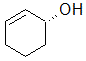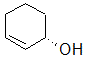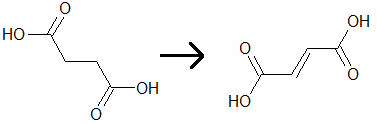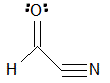|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
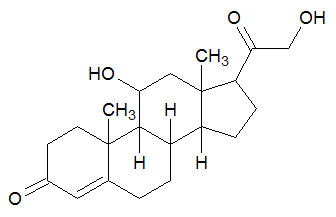
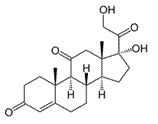
Cortisone is a steroid hormone, a modified cholesterol molecule. How many chiral centers does cortisone have?
 |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
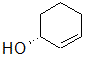
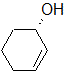
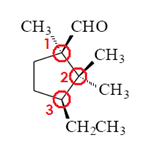
Label each of the three circled carbons with the appropriate chirality: R, S, or not chiral.
 |
|
A
|
1:R 2:Not chiral 3:R |
B
|
1:R 2:Not chiral 3:S |
C
|
1:S 2:Not chiral 3:S |
D
|
1:S 2:R 3:S |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following correctly lists the ions in order from smallest to largest? |
|
A
|
S2-, Cl-, Ca2+, K+ |
B
|
Ca2+, K+, Cl-, S2- |
C
|
Cl-, S2-, Ca2+, K+ |
D
|
S2-, Cl-, K+, Ca2+ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
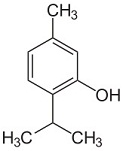
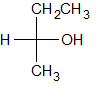
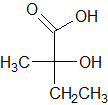
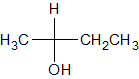
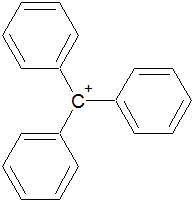
The following molecule contains all of which list of functional groups?
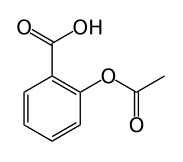 |
|
A
|
carboxylic acid, ester |
B
|
alcohol, ketone, ester |
C
|
carboxylic acid, ether, ketone |
D
|
alcohol, ketone, ether |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Carboxylic Acids | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
When a neutral metal sphere is charged by contact with a positively charged glass rod, the sphere |
|
A
|
loses protons |
B
|
loses electrons |
C
|
gains protons |
D
|
gains electrons |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
If two particular isomers of a compound are epimers, then what other stereochemical relationship do these compounds have?
|
|
A
|
They are enantiomers of each other |
B
|
They are conformers of each other |
C
|
They are diastereomers of each other
|
D
|
They are tautomers of each other |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
The R enantiomer of compound X rotates light +10 degrees. If a solution is made of 75% the R enantiomer and 25% the S enantiomer, what is the expected rotation of light for the solution? |
|
A
|
+2.5 degrees |
B
|
+3.8 degrees |
C
|
+5 degrees |
D
|
+7.5 degrees |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules has 3 groups of chemically equivalent hydrogen atoms? |
|
A
|
Cyclohexane |
B
|
2-methylbutane |
C
|
2,3-dimethylbutane |
D
|
Pentane
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which molecule contains a total of three carbon atoms? |
|
A
|
2-methylpropane |
B
|
2-methylbutane |
C
|
propane |
D
|
butane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular molecule is under study. Based on various data, it is discerned that a particular carbon is an R-stereocenter. Which of the following can be confirmed about the molecule, assuming that the molecule contains only one stereocenter? |
|
A
|
The molecule will rotate light clockwise |
B
|
The molecule will rotate light counterclockwise |
C
|
The molecule will not result in any light rotation |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many 1s orbitals does any given atom have? |
|
A
|
1 |
B
|
2 |
C
|
Depends on the number of electrons |
D
|
Depends on the atomic number |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following nucleophiles would be easily initiate an SN2 reaction with a tertiary alkyl halide? |
|
A
|
OH- |
B
|
OCH3- |
C
|
OC(CH3)3- |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
A certain biological molecule, compound Z, has the empirical chemical formula C18H24O13. The molecule is noted as having three chiral centers. How many molecules different from compound Z contain identical connectivity? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
Phosphorus had 3 allotropes: red, white, and black.
White is most reactive due in large part to having 60
degree bonds in a tetrahedral formation. Which of the
following best explains the reason for the bond angle
increasing reactivity? |
|
A
|
60 degree angles are energetically favorable, making
the allotrope less stable and thus more reactive. |
B
|
60 degree angles are energetically unfavorable, making
the allotrope less stable and thus more reactive. |
C
|
60 degree angles are energetically favorable, making
the allotrope more stable and thus more reactive. |
D
|
60 degree angles are energetically unfavorable, making
the allotrope more stable and thus more reactive. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
The S enantiomer of a compound rotates light +10 degrees. If a solution is made of 75% the R enantiomer and 25% the S enantiomer, what is the expected rotation of light for the solution? |
|
A
|
-7.5 degrees |
B
|
-5 degrees |
C
|
5 degrees |
D
|
7.5 degrees |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
Photons are often emitted during changing energy states within atoms. These changing energy states involve |
|
A
|
electrons |
B
|
protons |
C
|
neutrons |
D
|
positrons |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
The mirror image of a carbon with sp2 hybridization is its |
|
A
|
enantiomer |
B
|
tautomer |
C
|
diastereomer |
D
|
none of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the two cyclohexane derivatives below is more stable?
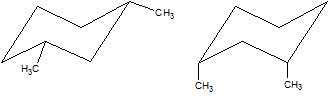 |
|
A
|
Both are equally stable |
B
|
Both are very unstable |
C
|
The structure on the left is more stable |
D
|
The structure on the right is more stable |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 49 |
Go |
Q:
|
Hund's rule states that: |
|
A
|
electrons fill orbitals from the lowest energy to highest energy |
B
|
electrons are paired with each other with the same spin in orbitals |
C
|
electrons are promoted to higher energy levels only when illuminated by light of specific frequency |
D
|
electrons do not pair with each other in an orbital until all orbitals in the subshell have one electron of the same spin |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which conformational isomer of butane has the highest potential energy? |
|
A
|
anti-staggered |
B
|
gauche |
C
|
eclipsed |
D
|
fully eclipsed |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 51 |
Go |
Q:
|
A 20.0 eV photon collides with a hydrogen atom which was initially in
ground state (with an ionization potential of 13.6 eV). Calculate the kinetic energy of the ejected electron.
|
|
A
|
6.4 eV |
B
|
13.6 eV |
C
|
20.0 eV |
D
|
33.6 eV |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which is a feature of alkali metals? |
|
A
|
They have a single electron in their valence shell |
B
|
They have the highest ionization enthalpies in each period |
C
|
This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table |
D
|
They have a high melting point |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Periodic Table | |
|
| 53 |
Go |
Q:
|
One of the steps of the citric acid cycle is the conversion of succinate to fumarate, which results in the reduction of FAD. This process is shown by the diagram below. Which of the following statements is(are) true regarding the reaction that occurs?
I. Fumarate will rotate polarized light differently than succinate does.
II. FAD becomes reduced to FADH2
III. The chemical potential energy of fumarate is lower than succinate.
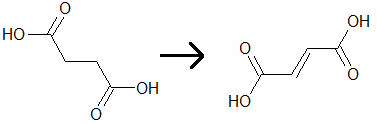 |
|
A
|
III only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Citric Acid Cycle | Atomic & Electronic Structure | Redox Reactions | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
Sam and Molly are working on a science project together, observing the movement of electrons. They have found the velocity of the electron 4 seconds into the experiment. Sam believes that he can use this information to determine the electron's location. Is Sam correct? Why or why not? |
|
A
|
He is incorrect because the mass of an electron is always the same. |
B
|
Sam is mistaken and we cannot know where the electron is. |
C
|
He is correct because the electron follows a known path. |
D
|
He is correct because electrons exhibit wave-like properties. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is most reactive when combined with an electrophile? |
|
A
|
3-methylbut-1-ene |
B
|
2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene |
C
|
transbut-2-ene |
D
|
propene |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following pairs of monosaccharides are anomers? |
|
A
|
β-D-glucopyranose and β-D-mannopyranose |
B
|
β-D-glucopyranose and α-D-mannopyranose |
C
|
β-D-glucopyranose and α-D-glucopyranose |
D
|
β-D-glucopyranose and β-L-glucopyranose |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 58 |
Go |
Q:
|
A central carbon is attached to four different substituents: bromine, chlorine, fluorine and hydrogen. If the hydrogen were to point towards you, the order of the remaining three substituents in clockwise order would be chlorine, fluorine and then bromine. What is the absolute configuration of this molecule? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 59 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is optically inactive? |
|
A
|
a meso compound |
B
|
a compound with three chiral centers |
C
|
a mixture of enantiomers in unequal proportions |
D
|
a central carbon attached to hydrogen, chlorine, iodine, and bromine |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 60 |
Go |
Q:
|
Comparing cis-1,2-dibromoethene to trans-1,2-dibromoethene, which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
trans-1,2-dibromoethene has a dipole moment while cis-1,2-dibromoethene does not |
B
|
trans-1,2-dibromoethene experiences more steric hindrance than cis-1,2-dibromoethene |
C
|
cis-1,2-dibromoethene has a higher boiling point than trans-1,2-dibromoethene |
D
|
both compounds have identical physical and chemical properties |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 61 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following represents the likely order of ion size from smallest to largest? |
|
A
|
I-, Te2-, Rb+, Br- |
B
|
Rb+, Br-, I-, Te2- |
C
|
Br-, Rb+, Te2-, I- |
D
|
Te2-, I-, Br-, Rb+ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 64 |
Go |
Q:
|
For an element whose valence electron configuration is ns2np1, where n is some integer, how will its electron affinity compare to its neighboring element whose electron configuration is ns2np2? |
|
A
|
It will be lower because electron affinity increases as one goes right and up along the periodic table |
B
|
It will be higher because electron affinity increases as one goes right and up along the periodic table |
C
|
It will be higher because electron affinity decreases as one goes right and up along the periodic table |
D
|
It will be lower because electron affinity decreases as one goes right and up along the periodic table |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 65 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which orbital(s) exist in Chromium's (atomic number 24) highest energy level? |
|
A
|
s |
B
|
p |
C
|
d |
D
|
A combination of one or more of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 66 |
Go |
Q:
|
Free radicals are often highly reactive species that have an imbalance in their electronic structure. This imbalance is due to free radicals |
|
A
|
having nonzero oxidation numbers |
B
|
being charged |
C
|
free radicals having unpaired electrons |
D
|
having too many electrons in their valence shell |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 67 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following conditions decreases the nucleophilicity of a compound? |
|
A
|
decrease in steric hindrance |
B
|
decrease in electron density |
C
|
increase in its strength as a base |
D
|
increase in its electron-density donating groups |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 68 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the shapes of s-orbitals and p-orbitals, which of the following hybridized orbitals is most spherical? |
|
A
|
sp3 |
B
|
sp2 |
C
|
sp |
D
|
All of the above have identical spherical shape |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 70 |
Go |
Q:
|
The valence band of an atom is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present. The conduction band is the range of energies where electrons are free enough to move delocalized from atom to atom. However, not all elements have electrons that lie within their conduction bands. Which of the following elements would be expected to have its valence band and its conduction bands overlapping? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Periodic Table | |
|
| 71 |
Go |
Q:
|
According to VSEPR theory, what is the electron pair geometry of NH3? |
|
A
|
bent |
B
|
linear |
C
|
trigonal planar |
D
|
tetrahedral |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 72 |
Go |
Q:
|
Metallic hydrogen is a theoretical phase of hydrogen that is predicted to form at ultra-high pressures. In this state of matter, electrons are delocalized. For gas giants like Jupiter, composed primarily of hydrogen, is known to have a spinning core. One key observation is that Jupiter also has a very strong magnetic field. This magnetic field is most likely caused by: |
|
A
|
Hydrogen, which has nonzero magnetic momentum of its sole electron, is inherently magnetic. |
B
|
The spinning of the metallic core creates a current, which in turn generates a magnetic field. |
C
|
The magnetic field is caused by spinning of the hydrogen nucleus. |
D
|
Delocalized electrons always produce a magnetic field. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 73 |
Go |
Q:
|
HCl has a lower boiling point than HI even though HCl has a stronger dipole moment. The reason for the higher boiling point of HI is primarily: |
|
A
|
Iodine is substantially larger than Chlorine. |
B
|
Iodine is less electronegative than Chlorine. |
C
|
Iodine has more unstable (radioactive isotopes than Chlorine). |
D
|
Iodine has more valence electrons than Chlorine. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 75 |
Go |
Q:
|
A molecule with square planar geometry, like XeF4 has different geometry from SiCl4 because: |
|
A
|
Xe is an inert gas. |
B
|
Fluorine is more electronegative than Xenon. |
C
|
The bond angles for the square planar geometry are larger than for the tetrahedral geometry, making XeF4 more stable as a square planar molecule. |
D
|
XeF4 has two lone pairs in addition to the four bonds. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 77 |
Go |
Q:
|
A photon strikes an atom with 12.8 eV of energy. As a result, the atom emits another photon and has an electron excited to an energy level that is 11.4 eV higher. With what energy is the atom's photon emitted? |
|
A
|
1.4 eV |
B
|
11.4 eV |
C
|
12.8 eV |
D
|
14.2 eV |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 78 |
Go |
Q:
|
Despite having many more protons in the nucleus and a greater nuclear charge, Cs has a much lower ionization energy than Li. This difference can be most attributed to which of the following? |
|
A
|
difference in elemental density |
B
|
difference in atomic radius |
C
|
difference in periodic table group |
D
|
difference in elemental reactivity |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 79 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following electron configurations depicts an atom in an excited state? |
|
A
|
1s22s22p63s23p64s1 |
B
|
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d1 |
C
|
1s22s22p63s23p64s13d1 |
D
|
1s22s22p63s23p5 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 80 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following represents the correct ground state electronic configuration for ferrous ion, Fe2+? |
|
A
|
[Ar]4s23d6 |
B
|
[Ar]4s23d4 |
C
|
[Ar]3d6 |
D
|
[Ar]4s23d2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 82 |
Go |
Q:
|
Mercury has the lowest boiling point of any metal in large part due to the fact that it does not share electrons well with its neighboring atoms. Based on this information, we can conclude that compared to similar metals, mercury has a low: |
|
A
|
ionization energy. |
B
|
density. |
C
|
electrical conductivity. |
D
|
molecular weight. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 83 |
Go |
Q:
|
In which orbital(s) would you expect to find the valence electrons of In? |
|
A
|
5s only |
B
|
5s and 5p only |
C
|
5s, 4d, and 5p |
D
|
5s, 5d, and 5p |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 87 |
Go |
Q:
|
Under which conditions is the second ionization energy for an atom greater than its first ionization energy? |
|
A
|
Only if the atom has an odd number of valence electrons. |
B
|
Only if the atom has one valence electron. |
C
|
Only if the atom is a nonmetal. |
D
|
The second ionization energy for an atom is always greater than its first. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 90 |
Go |
Q:
|
The frequency of a photon emitted from an electron transition in an atom is directly proportional to: |
|
A
|
the energy drop of the electron. |
B
|
the number of electrons the atom has. |
C
|
the number of valence electrons the atom has. |
D
|
the velocity of the photon. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 91 |
Go |
Q:
|
The nuclear charge of an atom will most directly influence which of the following properties? |
|
A
|
number of valence electrons |
B
|
atomic radius |
C
|
VSEPR configuration |
D
|
elemental reactivity |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 92 |
Go |
Q:
|
Line-emission spectra are an easy way of identifying elements in a sample by identifying the unique wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation emitted. The emissions are a result of which of the following? |
|
A
|
Electron moving from high energy to low energy |
B
|
Electron moving from low energy to high energy |
C
|
Electron release from the nucleus as a β- emission |
D
|
Energy released during nuclear electron capture |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 96 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the correct electron configuration for a chloride ion (Cl-)? |
|
A
|
[Ne]3s23p5 |
B
|
[Ne]3s22d103p5 |
C
|
[Ne]3s23p6 |
D
|
[Ne]3s22d103p6 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 98 |
Go |
Q:
|
An aurora, like the Northern Lights, is caused by high energy particles interacting with atmospheric gasses like nitrogen and oxygen. These gases emit the light when which of the following occurs? |
|
A
|
The charged particles enter the vicinity of the gas molecules. |
B
|
The electrons in the gas atoms are excited to a high energy state. |
C
|
The electrons in the gas atoms drop from a high to a low energy state. |
D
|
The electrons in the gas atoms are lost. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 99 |
Go |
Q:
|
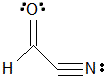
Given the molecule below, which of the following correctly lists the hybridizations of the three main atoms (carbon, nitrogen, nitrogen) from left to right?
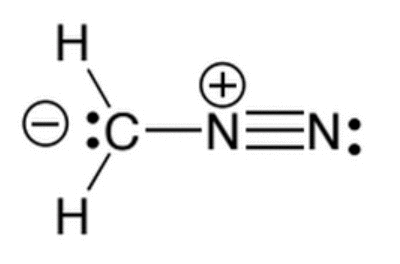
|
|
A
|
sp2, sp2, sp
|
B
|
sp2, sp, sp2
|
C
|
sp2, sp, sp
|
D
|
sp, sp, sp
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 100 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two experiments provide an emission and absorption spectrum for hydrogen. The emission spectrum is found by analyzing the light from hydrogen gas that is heated to high temperatures, while the absorption spectrum is found by passing incandescent light through hydrogen gas. Which of the best describes the absorption spectrum if it is obtained at room temperature? |
|
A
|
The absorption spectrum contains all the same lines as the emission spectrum |
B
|
The absorption spectrum is missing some of the lines that the emission spectrum has |
C
|
The absorption spectrum matches the emission spectrum, and even has some extra lines |
D
|
The absorption spectrum contains all the same lines as the emission spectrum, but they are phase-shifted |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 101 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, how many signals would be expected in the H-NMR and C-NMR data?
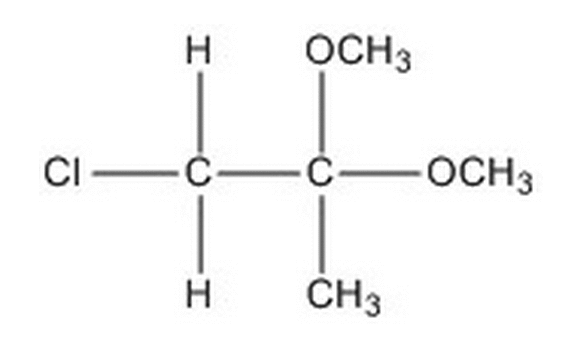 |
|
A
|
H-NMR: 3, C-NMR: 3
|
B
|
H-NMR: 3, C-NMR: 4
|
C
|
H-NMR: 4, C-NMR: 3
|
D
|
H-NMR: 3, C-NMR: 2
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 102 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, which of the following correctly describes the H-NMR and C-NMR data?
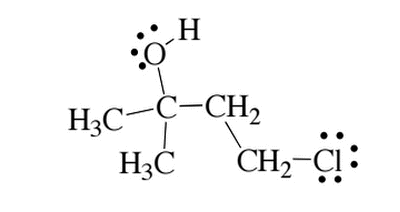 |
|
A
|
H-NMR absorption peaks: 3, C-NMR absorption peaks: 4
|
B
|
H-NMR absorption peaks: 4, C-NMR absorption peaks: 4
|
C
|
H-NMR absorption peaks: 4, C-NMR absorption peaks: 3
|
D
|
H-NMR absorption peaks: 3, C-NMR absorption peaks: 3
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 103 |
Go |
Q:
|
In describing the periodic trends of atomic radii, electron affinity, and first ionization energy, which of the following is correct going from left to right? |
|
A
|
The radius increases, the electron affinity decreases, and the first ionization energy increases
|
B
|
The radius increases, the electron affinity increases, and the first ionization energy decreases
|
C
|
The radius decreases, the electron affinity increases, and the first ionization energy increases
|
D
|
The radius decreases, the electron affinity decreases, and the first ionization energy increases
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Table | Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 105 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following orders carbon, silicon, and fluorine based on first ionization energies? |
|
A
|
Silicon > carbon > fluorine
|
B
|
Fluorine > carbon > silicon
|
C
|
Silicon > fluorine > carbon
|
D
|
Carbon > fluorine > silicon
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Periodic Table | |
|
| 106 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following represents the correct ground state electronic configuration for Fe3+? |
|
A
|
1s22s22p63s23p63d6
|
B
|
1s22s22p63s23p63d34s2
|
C
|
1s22s22p63s23p63d44s1
|
D
|
1s22s22p63s23p63d5
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Periodic Table | |
|
| 107 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best explains why the second ionization energy of Cs is higher than that of Ba? |
|
A
|
Ba is more electronegative than Cs. |
B
|
Cs has only 1 valence electron while Ba has 2. |
C
|
Cs has a lower atomic mass than Ba. |
D
|
The valance electrons of Ba are in a higher energy level than those of Cs. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 109 |
Go |
Q:
|
π-bonding for a covalent bond requires which of the following? |
|
A
|
Roughly equivalent electronegativities between the two atoms. |
B
|
Roughly equivalent atomic radii between the two atoms. |
C
|
The presence of an aqueous environment. |
D
|
The presence of a double or triple bond. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 113 |
Go |
Q:
|
The number of electrons in an energy shell is: |
|
A
|
1. |
B
|
2. |
C
|
4. |
D
|
contingent on the principle quantum number. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 115 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds contains the lowest carbon percent composition? |
|
A
|
methane |
B
|
ethane |
C
|
propane |
D
|
butane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 117 |
Go |
Q:
|
An organic molecule is found to be 7% hydrogen, 64% carbon, and 28% oxygen by mass. What is the empirical formula for the compound? |
|
A
|
C3H4O |
B
|
C3H2O2 |
C
|
C4H6O |
D
|
C4H3O2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 118 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two new atoms, X and Y, are discovered and it is noted that a variety of molecules can be formed via ionic bonds between these atoms. It is also found that the cationic form of X carries a +1 charge. Which of the following molecules would be expected to have the strongest ionic bond strength? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 119 |
Go |
Q:
|
A molecule with exactly one enantiomer can have how many stereocenters? |
|
A
|
Only one |
B
|
Any number greater than one |
C
|
One or more, but not zero |
D
|
Zero |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 120 |
Go |
Q:
|
Hydrogen is capable of having which of the following oxidation states?
I. -1
II. 0
III. 1 |
|
A
|
I and III only |
B
|
II and III only |
C
|
III only |
D
|
I, II and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 123 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds containing solely nitrogen and oxygen have an approximate percent composition of oxygen of 65%? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
| 124 |
Go |
Q:
|
When forming an ion, halogens will most likely: |
|
A
|
lose one electron. |
B
|
gain one electron. |
C
|
lose one neutron. |
D
|
gain one neutron. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|