|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two metal plates are placed in close proximity and are connected in a circuit with a battery. The capacitance of the plates is C. If area of the plates triples and the distance between them quadruples, what is the capacitance? |
|
A
|
9/4 C |
B
|
9/16 C |
C
|
3/4 C |
D
|
3/16 C |
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
A capacitor is placed in a circuit containing a 13 V battery. The capacitor is composed of two circular metal sheets of radius R separated by a distance D. If R is doubled and D is halved, what is the effect on capacitance? |
|
A
|
Remains constant |
B
|
Increases 2 times |
C
|
Increases 4 times |
D
|
Increases 8 times |
|
|
|
Tags:
Circuits | Magnetism | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given a charged particle with a certain velocity, which of the following best describes its resultant path after entering a uniform magnetic field with direction perpendicular to the particle? |
|
A
|
The particle's path will be a straight line
|
B
|
The particle's path will be parabolic sloping upwards
|
C
|
The particle's path will be parabolic sloping downwards
|
D
|
The particle's path will be a circle
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
An experiment shows that electron beams can pass undeflected through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. If changed, which of the following will NOT affect either the electric or magnetic forces? |
|
A
|
Sign of charge of the particles |
B
|
Magnitude of charge of the particles |
C
|
Mass of the particles |
D
|
Velocity of the particles |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electromagnetics | Magnetism | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
An electron moving with a velocity of 500 m/s in the x-direction enters a region filled with a constant magnetic field (B), which has a magnitude of 0.25 teslas and points into the page. The constant field region is 5 m long and 4 m wide and the electron enters 0.5 m from the top of the region. What is the magnitude of the electron's velocity when it leaves the region?
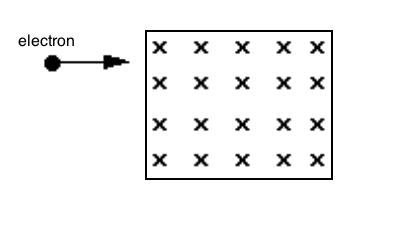 |
|
A
|
125 m/s |
B
|
250 m/s
|
C
|
500 m/s |
D
|
1,000 m/s |
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | Energy & Work | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two loops (shown below) carry equal current (I) in opposite directions. If the loops are held in parallel and then released, which of the following best describes their expected behavior? You may ignore any influence of gravity.
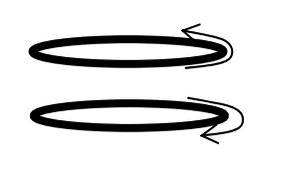 |
|
A
|
The loops will attract each other
|
B
|
The loops will repel each other
|
C
|
The loops remain in their same positions
|
D
|
The current in the top loop will gradually reverse its direction
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | Electrostatics | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A charged particle moving in the same direction as a magnetic field would experience: |
|
A
|
a force in the same direction as the magnetic field. |
B
|
a force in the opposite direction as the magnetic field. |
C
|
a force perpendicular to the magnetic field. |
D
|
no force due to the magnetic field. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Forces | Magnetism | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
A magnetic field of 15T is applied to a stationary charge of 2C in a controlled testing environment. Which of the following equates to the amount of force experienced by the charge? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
A proton moves down a piece of paper and a magnetic field is directed into the piece of paper. What is the direction of the magnetic force on this proton? |
|
A
|
out of the page |
B
|
up |
C
|
right |
D
|
left |
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A copper wire of length 20 cm conducts a current of 10 A. This current runs through a 3T magnetic field in a perpendicular fashion. Which of the following is the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire? |
|
A
|
0 N |
B
|
6 N |
C
|
120 N |
D
|
600 N |
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following correctly states the difference between a diamagnetic substance and a paramagnetic substance? |
|
A
|
all paramagnetic substances are diamagnetic |
B
|
all substances are considered paramagnetic |
C
|
magnetization of paramagnetic substances are not retained in the absence of an external magnetic field |
D
|
diamagnetism arises from unpaired electrons |
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|


