|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two bodies, one charged and one uncharged, come into contact. Which of the following options is (are) true regarding this event?
I. If either of the bodies are poor conductors, they will both retain their charge.
II. If both bodies are good conductors, they will both retain their charge.
III. If both bodies are good conductors, protons will move from the charged body to the uncharged body. |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II only |
C
|
I and III only |
D
|
II and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the equivalent resistance of the following network?
 |
|
A
|
158.66 ohms |
B
|
118.75 ohms |
C
|
0 ohms |
D
|
27 ohms |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
The potential at a point due to a unit positive charge is found to be V. If the distance between the charge and the point is quadrupled, the potential becomes |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
A point charge Q moves into an electric field E. A team of scientists want to see the behavior of the charge at the line labeled Z. Lab funds are very limited and it is desired to minimize energy costs. Which of the following paths, A or B, should the scientists choose in order to minimize the energy inputted?
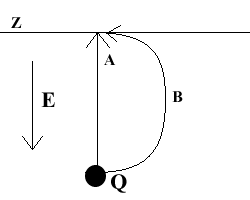 |
|
A
|
Both paths are equal in energetic input. |
B
|
Path A will minimize costs because it is the shortest path from the point charge to the line Z. |
C
|
Path B will minimize costs because it avoids going directly in the opposing electric field. |
D
|
Path A will minimize costs because it goes parallel to the electric field. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Energy & Work | Electrostatics | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
Moving 2.5 x 10-6 coulomb of charge from point A to point B in an electric field requires 6.3 x 10-4 joule of work. The potential difference between points A and B is approximately |
|
A
|
1.6 x 109 V |
B
|
4.0 x 103 V |
C
|
2.5 x 102 V |
D
|
1.0 x 1014 V |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two point charges are placed at a radius R from each other, and the force between them is F. If two point charges, each of magnitude double the initial point charges, are placed at a radius 2R from each other, what is the force between them?
|
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
Moving a 2 x 10-6 coulomb point charge from point X to point Y in an electric field requires 8 x 10-4 joule of work. The potential difference between points X and Y is approximately
|
|
A
|
4 x 10-2 V |
B
|
4 x 102 V |
C
|
4 x 103 V |
D
|
4 x 10-3 V |
|
|
|
Tags:
Energy & Work | Electrostatics | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
The distance between two electrically-charged objects triples. What is the new force between the two objects with respect to the original force? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the magnitude of force on an object with a charge of q = 2 in an electric field of 5 V/m? |
|
A
|
0.4 N |
B
|
1.25 N |
C
|
2.5 N |
D
|
10 N |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A object of mass M with charge Q rests on a concrete floor with a coefficient of static friction Z. Another charge of Q is placed a distance R away from the object. The object remains stationary. What is the magnitude force of static friction on the object? |
|
A
|
MZ |
B
|
kQ2/R2 |
C
|
kQ2Z/R2 |
D
|
kQZ/R2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Forces | Electrostatics | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
The potential at a point due to a unit positive charge is found to be V. If the distance between the charge and the point is quadrupled, the potential becomes |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
By how much does the strength of an electric field weaken when the distance from the point source is doubled? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
As the distance from a charged object triples, the voltage will |
|
A
|
increase by a factor of 3 |
B
|
increase by a factor of 9 |
C
|
decrease by a factor of 3 |
D
|
decrease by a factor of 9 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the voltage between two points separated by a distance of 10 cm in an electric field with a magnitude of 100 N/C parallel to the direction of the displacement between the two points? |
|
A
|
0 V |
B
|
10 V |
C
|
100 V |
D
|
1000 V |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following correctly describes how the electric potential changes with distance from a point charge? |
|
A
|
Electric potential decreases linearly with increasing distance. |
B
|
Electric potential is proportional to d2 |
C
|
Electric potential is proportional to 1/d |
D
|
Electric potential is proportional to 1/d2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
A positive (q0) and a negative charge (q1) are placed in an electric field at a distance r from each other. A scientist measures the attractive force between the two and determines it to be F0. What changes to the system can be made in order to double the original force between the two charges? |
|
A
|
Decrease q0 by half, and halve the original distance between the molecules |
B
|
Double the original distance, and double both of the original charges |
C
|
Halve the original forces, and decrease the distance by a factor of 4 |
D
|
Change q1 to a positive charge |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
A capacitor is made of two parallel plates, each with opposing and equal charges. Which of the following best describes the electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor when the plates are pulled apart until they are separated by a distance greater than their original distance?
|
|
A
|
The electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor is less than prior to the plates being pulled apart |
B
|
The electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor is the same as prior to the plates being pulled apart |
C
|
The electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor is greater than prior to the plates being pulled apart |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
A capacitor made of two parallel metallic plates (each with an opposing, equal surface charge density) has a metal block inserted between the plates, not touching or connecting to either plate. After the block is inserted, what will happen to the potential difference between the plates? |
|
A
|
The potential difference between the two plates will decrease |
B
|
The potential difference between the two plates will increase |
C
|
The potential difference between the two plates will stay the same |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
A positively charged insulating rod is put in close proximity to an object suspended by a string. If the object is attracted to the rod, which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
The object suspended by the string is an insulator |
B
|
The object suspended by the string is a conductor |
C
|
The object suspended by the string is negatively charged |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two loops (shown below) carry equal current (I) in opposite directions. If the loops are held in parallel and then released, which of the following best describes their expected behavior? You may ignore any influence of gravity.
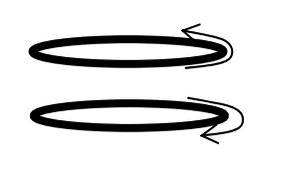 |
|
A
|
The loops will attract each other
|
B
|
The loops will repel each other
|
C
|
The loops remain in their same positions
|
D
|
The current in the top loop will gradually reverse its direction
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Magnetism | Electrostatics | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particle with a charge of +2.5C with a mass of 0.5kg enters an electric field with a strength of 4 N/C. Which of the following is the force exerted on the particle by the electric field? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that: |
|
A
|
momentum and velocity of an electron cannot be known at the same time. |
B
|
momentum and charge of an electron cannot be known at the same time. |
C
|
momentum and mass of an electron cannot be known at the same time. |
D
|
momentum and position of an electron cannot be known at the same time. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a vector?
I. capacitance
II. resistance
III. electric force |
|
A
|
I and III only |
B
|
II and III only |
C
|
III only |
D
|
I, II and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
A charge is displaced a specific distance in a uniform electric field and the potential energy of this charge is noted to be X. If the charge is displaced double the distance, the potential energy would be expected to be: |
|
A
|
X/4. |
B
|
X/2. |
C
|
2X. |
D
|
4X. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the frequency of a wave traveling at a wavelength of 10 km? |
|
A
|
3 x 104 s-1 |
B
|
3 x 105 s-1 |
C
|
3 x 106 s-1 |
D
|
3 x 107 s-1 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is false regarding equipotential lines between two plates of a capacitor? |
|
A
|
The work it would take to move a charge from one equipotential line to another line is independent of path. |
B
|
Electric potential at each point on an equipotential line is the same value. |
C
|
The equipotential lines are non-curved, straight lines. |
D
|
The lines run perpendicular to the plate. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
A cyllindrical wire with a radius of 0.002m, resistance of 2 ohms, and a length of 0.01 m is examined. What is the resistivity of the wire? |
|
A
|
1.5*10-3 ohm*m |
B
|
2.5*10-3 ohm*m |
C
|
3.5*10-3 ohm*m |
D
|
4.5*10-3 ohm*m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
The units for the concept of electromotive force is given as: |
|
A
|
newtons. |
B
|
newton * meters. |
C
|
current/resistance. |
D
|
volts. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Each plate of a capacitor is measured to have a charge of 5 mA and a resultant voltage of 10 mV. Which of the following is the capacitance of this system? |
|
A
|
1 mF |
B
|
1 F |
C
|
0.5 mF |
D
|
0.5 F |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | Circuits | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Reduction potential most closely resembles the concept of: |
|
A
|
ionization energy. |
B
|
oxidation state. |
C
|
electron affinity. |
D
|
polarization. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electrostatics | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|



