|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
A simple pendulum has a mass M attached to its end. Its period of oscillation on Earth is T. The pendulum is taken to a different planet where the gravity is one fourth of Earth's. Also, the length of the string doubles, and another mass M (thus there is a total mass of 2M on the pendulum) is placed on the pendulum. What is the ratio of the period of oscillation on Earth to the period of oscillation on this new planet? |
|
A
|
1 : √8 |
B
|
1: 2 |
C
|
1 : √2 |
D
|
Cannot be determined with the information provided. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the period of a wave if 50 crests pass an unmoving point over the course of 20 seconds? |
|
A
|
1000 seconds |
B
|
2.5 seconds |
C
|
0.4 seconds |
D
|
1/1000 seconds |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
A ball massing 10 kg hangs at the end of a massless, 5m string. The ball is then set swinging with a maximum velocity of 5 m/s. What is the maximum tension in the rope? |
|
A
|
100 N |
B
|
150 N |
C
|
175 N |
D
|
300 N |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | Forces | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following simple pendulum is set up:
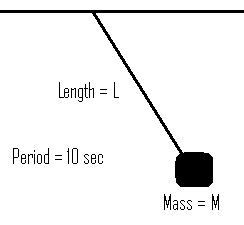
If the length of the string quadrupled and the mass attached was halved, what would be the new period
and frequency? |
|
A
|
Period = 5 sec, Frequency = 0.5 Hz |
B
|
Period = 10 sec, Frequency = 0.1 Hz |
C
|
Period = 5 sec, Frequency = 1 Hz |
D
|
Period = 20 sec, Frequency = 0.05 Hz |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
A vibrating string is behaving like a standing wave with nodes at the ends and 3 antinodes. The string is 150 cm long and the wave travels at 20 m/s. What is the string vibration wavelength and frequency? |
|
A
|
0.75 m, 26.6 Hz |
B
|
1.5 m, 15 Hz |
C
|
2 m, 20 Hz |
D
|
1 m, 20 Hz |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following statements is false regarding the diagram shown below, assuming the object obeys Hooke's law and at t=0, is at its point of equilibrium?
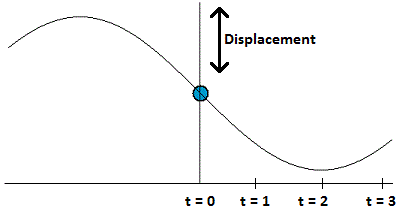 |
|
A
|
Assuming no friction, the object is in simple harmonic motion |
B
|
At t=0, the acceleration is in the negative y direction |
C
|
At t=1, the acceleration is in the positive y direction |
D
|
At t=2, the acceleration is in the positive y direction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following does not depend on the mass of the object involved? |
|
A
|
the period of a pendulum composed of a 500g ball at the end of a string |
B
|
the period of a horizontal spring attached to a 1 kg weight |
C
|
the period of a vertical spring attached to a 750g weight |
D
|
the frictional force on a 100 kg mass a sliding down an incline with a coefficient of kinetic friction
of 0.28 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Forces | Periodic Motion | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
The third harmonic of a standing wave between two walls has a wavelength of 1.5 m. What is the distance between the walls? |
|
A
|
0.5 m |
B
|
1.5 m |
C
|
2.25 m |
D
|
4.5 m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
A spring oscillates on a horizontal frictionless surface. At the end of the spring is attached a block of mass M. For any given spring extension, by how much does the spring potential energy change if the mass M is doubled to 2M? |
|
A
|
The energy halves. |
B
|
The energy remains the same. |
C
|
The energy doubles. |
D
|
The energy quandruples. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Energy & Work | Periodic Motion | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
At what magnitude of extension is the kinetic energy equal to the spring potential energy of a mass on the end of a spring where the spring constant is 700 N/m, and total energy is 1000 J? |
|
A
|
1.19 m |
B
|
1.43 m |
C
|
2.05 m |
D
|
2.54 m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
A spring with a 1kg mass attached to it oscillates with an amplitude of 15 cm. The frictionless surface on which it oscillates is replaced with a surface with a μk of 0.25. If the spring oscillates through 20 periods before coming to a halt, what was the original energy of the system? Assume each of the 20 periods covers the same distance. |
|
A
|
7.5 J |
B
|
15 J |
C
|
30 J |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
A 5m massless string is set up with a mass of 5 kg on the end. The mass is swung like a pendulum and at its maximum amplitude reaches 90° to either side of its resting position. What is the maximum tension generated on the string during its swing? |
|
A
|
50 N |
B
|
100 N |
C
|
150 N |
D
|
500 N |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
A spring in simple harmonic motion is synchronized with the motion of a pendulum. The masses on the spring and the pendulum are identical. If the masses on the ends are doubled, what will happen to the synchronization? |
|
A
|
The pendulum will have a period that is greater than that of the spring |
B
|
The pendulum will have a period that is less than that of the spring |
C
|
The period of the spring will decrease |
D
|
The period of the pendulum will increase |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two ornaments are hanging from the ceiling, attached by springs with the same spring constant. Ball A masses 3kg and ball B masses 6kg. If ball A deforms the spring 5 cm from normal, how far down is ball B hanging from normal? |
|
A
|
5 cm |
B
|
8 cm |
C
|
10 cm |
D
|
15 cm |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
A simple pendulum oscillates with a period T. It has a length of L a weight at the end of the pendulum with a mass of M. What mass would the weight need to be in order for the pendulum to oscillate with a period of T/2? |
|
A
|
2M |
B
|
M/2 |
C
|
M/4 |
D
|
There is no mass that can be added to cause the pendulum to oscillate with a period of T/2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
A pendulum with a mass m moves with a period of 4 seconds, measured on Earth assuming gravity = 10 m/s2. If the mass on the pendulum is quadrupled, what will the period of the pendulum become? |
|
A
|
1 second |
B
|
4 seconds |
C
|
16 seconds |
D
|
48 seconds |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
The next MCAT eCourse starts tomorrow! Come see how we can help improve your score.
A mass oscillating in simple harmonic motion on a spring achieves a maximum velocity of 2 m/s with a total system energy of 320 J. If the spring constant is k = 10 N/m, what is the period of the spring? Note: the period of a spring is given by the equation T = 2π√(m/k) |
|
A
|
8 s |
B
|
25 s |
C
|
4 s |
D
|
32 s |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
A pendulum is being built to have a period as consistent as possible over time. It will be built with a heavy mass and nearly massless string, and oscillate in a vacuum. Which of the following external parameters must be most closely controlled to maintain its period? |
|
A
|
Illumination of the system |
B
|
Elevation of the system |
C
|
Mass at the tip of the pendulum |
D
|
Sound energy provided to the system |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
In order to double the period of a pendulum, one would have to: |
|
A
|
double the length of the pendulum. |
B
|
quadruple the length of the pendulum. |
C
|
double the gravitational constant. |
D
|
quadruple the gravitational constant. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
A simple pendulum consists of mass m and length L. If the mass and pendulum length are doubled, the period will:
|
|
A
|
Increase by a factor of 1.4 |
B
|
Increase by a factor of 2 |
C
|
Decrease by a factor of 1.4 |
D
|
Decrease by a factor of 4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Quantitative Skills | Energy & Work | Periodic Motion | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
A block is attached to an ideal spring that is suspended from a ceiling. The block oscillates with a period of 20 seconds. If the acceleration due to gravity was reduced by 50%, the block's period would equal: |
|
A
|
5 seconds.
|
B
|
10 seconds.
|
C
|
20 seconds.
|
D
|
40 seconds.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
A pendulum that exhibits periodic motion:
|
|
A
|
will have zero potential energy at its peak height. |
B
|
will have zero kinetic energy at its peak height.
|
C
|
will have zero velocity when its displacement is minimized.
|
D
|
will move faster as its distance from the equilibrium position increases.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Energy & Work | Periodic Motion | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a transverse wave? |
|
A
|
A shock wave through the air. |
B
|
A sound wave. |
C
|
A vibrating string on a musical instrument. |
D
|
Pressure wave through a liquid. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
A string of length 1 m is vibrated once every other second, creating waves of wavelength 10 mm. How many waves would be expected to traverse the entire length of the string in one minute? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
A spring is suspended from the ceiling and a weight is attached to the bottom. The spring is displaced from equilibrium and released which results in a simple harmonic motion of the spring and mass system. During this motion, at zero displacement from equilibrium, which of the following values are non-zero with respect to the mass?
I. momentum
II. velocity
III. elastic force acting on the mass |
|
A
|
II only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following terms determines the period of oscillation for a pendulum?
I. mass of pendulum
II. acceleration due to gravity
III. length of pendulum |
|
A
|
II only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Motion | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|


