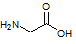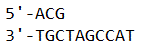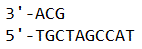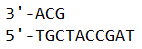|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
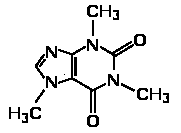
Under testing, chromosomal DNA of an unknown organism is shown to have an unusually large amount of repetition of several nucleotides at the ends. Identify what this repetition is and what does it imply about the eukaryote?
|
|
A
|
The repetition is a telomere. The repetition implies that the cell undergoes frequent replication, and thus has long telomeres to prevent rapid erosion of the chromosomes.
|
B
|
The repetition is an Okazaki Fragment. The repetition implies that the cell undergoes frequent replication, and thus has extra long telomeres to prevent rapid erosion of the chromosomes.
|
C
|
The repetition is a telomere. The repetition implies that the chromosome contains a significant amount of excess genomic data, much of which is never translated.
|
D
|
The repetition is the promoter region of the chromosome. The repetition implies that the chromosome contains a significant amount of excess genomic data, much of which is never translated.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | Eukaryotic Cells | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
A transcriptional error in the production of a particular protein results in the substitution of a glycine. Which of the following amino acids would be least harmful if put in the place of glycine (shown below)?
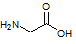
|
|
A
|
Arginine:
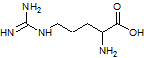 |
B
|
Tyrosine:
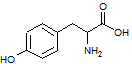 |
C
|
Alanine:
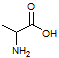 |
D
|
Cysteine:
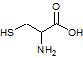 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
RNA can be seen to degrade if left at room temperature for too long, while DNA does not have this issue. The major reason for this is that |
|
A
|
The DNA backbone provides additional stability that the RNA backbone does not provide. |
B
|
The replacement of thymine with uracil decreases the stability of the RNA molecule. |
C
|
DNA is wound more tightly around itself in a different manner than RNA, providing it increased stability. |
D
|
DNA is a more stable molecule than RNA |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | Alcohols | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A molecule of DNA is slowly heated. The base pairs are closely examined. It is noted that |
|
A
|
The Adenine and Thymine bonds break before the Guanine and Cytosine bonds. |
B
|
The Guanine and Cytosine bonds break before the Adenine and Thymine bonds. |
C
|
Bond breaking occurs all at a single temperature. |
D
|
Bond breaking occurs at the sites of weakest interaction but has no relation to the individual base pairs. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following interactions result in the specificity and tight binding of the two strands in the DNA double helix? |
|
A
|
London dispersion forces |
B
|
Covalent bonding |
C
|
Hydrogen bonding |
D
|
Dipole-dipole interactions |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A major structural difference between tRNA and mRNA is: |
|
A
|
tRNA lacks uracil while mRNA does not lack uracil |
B
|
tRNA is synthesized in the nucleus while mRNA is synthesized by ribosomes |
C
|
mRNA is used by mitochondria while tRNA is used by the nucleus |
D
|
mRNA primarily has a linear conformation while tRNA primarily has a complex tertiary structure |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Depending on the nucleotides in a specific strand of DNA, the strands will split at different temperatures. The major cause for this is |
|
A
|
Differences in phosphate amounts on the backbone |
B
|
Differences in G-C and A-T content |
C
|
The width of helix depends on the nucleotide sequence |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
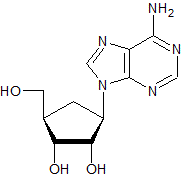
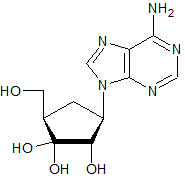
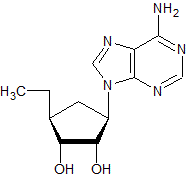
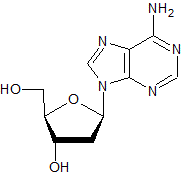
The structure of adenosine (with its ribose sugar) is given below. Which of the following structures depicts deoxyadenosine (with its deoxyribose sugar)?
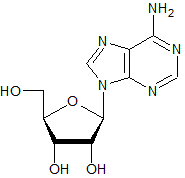 |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds would be an effective nuclear stain? |
|
A
|
Osmium tetroxide, a dark colored dye which reacts with lipid-dense structures |
B
|
DAPI, a fluorescent stain which binds strongly to purines and pyrimidines |
C
|
Carmine, a red dye which binds strongly to polysaccharide |
D
|
Bismark brown, a yellow dye which stains high-molecular-weight glycoproteins
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Histones are proteins that closely associate with the DNA of eukaryotes. Which of the following best describes the physical properties of histones given their close association with DNA? |
|
A
|
positively-charged |
B
|
negatively-charged |
C
|
highly nonpolar |
D
|
their physical properties are highly variable based on the genes with which they associate |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
In ddNTP DNA sequencing, dideoxynucleotides are used to terminate the replication of DNA strands which can then be analyzed for their length on gel electrophoresis. The ddNTPs are missing both their 2' and 3' hydroxyl groups. Which of the following reasons best explains why ddNTPs terminate the DNA replication? |
|
A
|
Nucleotides must have a 3' hydroxyl group for extension of the fragment to occur. |
B
|
Nucleotides must have a 2' hydroxyl group for extension of the fragment to occur. |
C
|
The loss of two hydroxyl groups makes the terminal end of the DNA nonpolar and thus unable to continue extending. |
D
|
ddNTPs are always used by cells for termination of their DNA replication strands. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | DNA Replication and Repair | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
Histones are closely associated with DNA in chromatin. Which of the following best describes the physical properties of histones? |
|
A
|
Histones are largely positively charged. |
B
|
Histones are largely negatively charged. |
C
|
Histones are largely nonpolar. |
D
|
Histones are translated by ribosomes into the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
Compared to eukaryotic cell, a virus composed exclusively of DNA and protein should have a disproportionately high percentage of which element by mass (dry weight)? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
SDS is a negatively charged detergent used to disrupt noncovalent bonds between amino acids in a protein. One molecule of SDS binds on average to two residues of a protein. The protein segments are then separated by gel electrophoresis (an electric field is applied to the gel containing the protein segments) on the basis of molecular weight. The rate of movement of the protein through the gel is inversely proportional to the log of the molecular weight.
The separation of nucleic acids by electrophoresis does not require SDS. Why?
|
|
A
|
There are no residue groups on nucleic acids to which SDS can bind |
B
|
Nucleic acids can separate based on their hydrophobicity without the binding of SDS |
C
|
Nucleic acids have phosphate groups that contribute net negative charges proportional to their size |
D
|
Nucleic acids do not have tertiary structures like protein that need to be disrupted |
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding using dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) for DNA sequencing?
|
|
A
|
Restriction enzymes cut the target DNA into fragments, which are then separated and visualized with electrophoresis
|
B
|
The template strand is tagged with a radioactive isotope
|
C
|
ddATPs, ddCTPs, ddGTPs, and ddTTPs must be utilized in a separate environment from the dATPs, dCTPs, dGTPs, and dTTPs
|
D
|
A ddTTP can randomly and occasionally terminate the synthesis of DNA where an adenine occurs in the template strands
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology | Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | DNA Replication and Repair | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best describes how tRNA differs from mRNA? |
|
A
|
Transfer RNA uses adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine while messenger RNA uses adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine.
|
B
|
Transfer RNA uses adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine while messenger RNA uses adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine.
|
C
|
Transfer RNA has a complex loop structure while messenger RNA is usually a simple, linear strand.
|
D
|
In transfer RNA, anticodons are complementary to messenger RNA codons, while in messenger RNA, codons are anti-complementary to DNA triplets.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Genetic Code, Transcription, Translation | Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular template DNA strand (noncoding strand) is composed of 18% cytosine and 20% guanine. What percentage of its RNA transcript will contain cytosine assuming no introns are removed? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT a difference between DNA and RNA? |
|
A
|
DNA contains thymine while RNA contains uracil. |
B
|
In its native form, RNA is generally single-stranded while DNA is generally double-stranded. |
C
|
RNA can be translated directly into protein while DNA cannot. |
D
|
RNA lacks a 2' OH while DNA has a 2' OH. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
DNA strands with higher percentages of G and C nucleotides have higher melting temperatures than strands with higher percentages of A and T nucleotides. This is because: |
|
A
|
G and C nucleotides form covalent bonds while A and T nucleotides form hydrogen bonds. |
B
|
G and C nucleotides are smaller and thus more closely packed together. |
C
|
G and C nucleotides form 3 hydrogen bonds while A and T nucleotides form only two. |
D
|
G and C nucleotides are larger and thus have higher boiling points. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following types of bonds is responsible for binding of purines with pyrimidines? |
|
A
|
Van der waals forces |
B
|
hydrogen bonds |
C
|
covalent bonds |
D
|
polar bonds |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following DNA strands will have the lowest melting temperature? |
|
A
|
20% thymine |
B
|
25% cytosine |
C
|
30% guanine |
D
|
35% adenine |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
An RNA molecule is examined and it is found that a small percentage of pairs are G-U base pairs. This serves as an example of: |
|
A
|
wobble pairing. |
B
|
inconsistent homology. |
C
|
non-Watsonian pairing. |
D
|
Hoogsteen base pairing. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
A strand-break temperature for a particular DNA molecule is defined as a temperature at which exactly 50% of the A-T bonds in a strand of DNA are split. If this temperature is 120 degrees celcius for a particular DNA strand, which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
greater than 50% of the C-G strands will be broken at the strand break temperature |
B
|
less than 50% of the C-G strands will be broken at the strand break temperature |
C
|
exactly 50% of the C-G strands will be broken at the strand break temperature |
D
|
we cannot know the status of the C-G strands from the information provided |
|
|
|
Tags:
Genetic Code, Transcription, Translation | Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|