|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following statements best describes the similarities between diacylglycerol and phospholipids? |
|
A
|
both have two glycerols acylated onto a fatty acid |
B
|
both have two fatty acids acylated onto gycerol |
C
|
both have a phosphate group on one of three hydroxyl groups on glycerol |
D
|
both have a sterol and fatty acid acylated onto glycerol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
The saponification value of triacylglycerides is a measure of the mass of NaOH required to detach, as sodium salts, the fatty acid chains from 1 gram of the triacylglycerides. Samples A and B have saponification values of 180 mg and 320 mg respectively. Which sample has longer fatty acid chains (on average) and why? |
|
A
|
A because the mass of NaOH required is directly proportional to the mass of fat based on the length of the fatty acid chains |
B
|
A because the mass of NaOH required is inversely proportional to the mass of fat based on the length of the fatty acid chains |
C
|
B because the mass of NaOH required is directly proportional to the mass of fat based on the length of the fatty acid chains |
D
|
B because the mass of NaOH required is inversely proportional to the mass of fat based on the length of the fatty acid chains |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
A micelle of a phospholipid forming in a solution of BF3 would be expected to have |
|
A
|
its polar heads on the inside of the complex |
B
|
its polar heads on the outside of the complex |
C
|
a mixed arrangement of heads and tails |
D
|
a complete dissociation of the micelle phospholipids |
|
|
|
Tags:
Membrane Transport and Signalling | Lipids | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Alkaline compounds often induce a slippery feel on the surface of skin. This process is in part due to the conversion of skin oils into surfactant molecules. This reaction can be best categorized as which of the following? |
|
A
|
aldol condensation |
B
|
saponification |
C
|
dehydrogenation |
D
|
decarboxylation |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A strong base is added to a triglyceride. This reaction can be best characterized as a |
|
A
|
Diels-Alder reaction |
B
|
condensation reaction |
C
|
saponification |
D
|
SN2 reaction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following describes the primary structural difference between phospholipids and triglycerides? |
|
A
|
Phospholipids are triglycerides with a phosphate attached at the end of the fatty acid tails. |
B
|
Triglycerides contain three fatty acid chains while phospholipids contain only two, with the third position being a phosphate group. |
C
|
Phospholipids are steroid compounds while triglycerides are fat compounds. |
D
|
Phospholipids use a 2-carbon compound to bind their fatty acids while triglycerides use a 3-carbon compound to bind their fatty acids. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
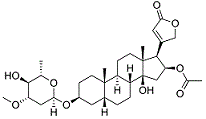
Oleandrin, shown above, affects cardiac function and is known as a cardiac glycoside. It can be identified as a glycoside due to the presence of a glycosidic bond. Oleandrin can also be classified as which of the following? |
|
A
|
polypeptide |
B
|
nucleic acid |
C
|
steroid |
D
|
triglyceride |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
The steroid hormones produced by the smooth endoplasmic reticulum would be stored in which of the following ways? |
|
A
|
Peroxisomes, so the hormones could aid in lipid breakdown. |
B
|
Steroid hormones are not stored; because they are lipophilic they are able to diffuse through lipid bilayers. |
C
|
Secretory vesicles, so the hormones could be released when needed. |
D
|
Lysosomes, so the hormone could aid in the breakdown and destruction of excess secretory products. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Membrane Transport and Signalling | Lipids | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Saponification occurs when a triglyceride is treated with which of the following? |
|
A
|
SOCl2 |
B
|
HCl |
C
|
NaBH4 |
D
|
NaOH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the best explanation for why animal fats (but not vegetable oils) are solid at room temperature? |
|
A
|
Animal fats have more double bonds than vegetable oils do
|
B
|
Animal fats have fewer double bonds than vegetable oils do
|
C
|
Animal fats have shorter fatty-acid tails than vegetable oils have
|
D
|
Animal fats have a lower concentration of sterols
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Phospholipids and fatty acids, and their degree of saturation, have far-reaching implications for membrane transport and fluidity. Which of the following is a correct statement? |
|
A
|
A saturated fatty acid has more double bonds than an unsaturated fatty acid |
B
|
A species in a cold environment will tend to have more double bonds in the fatty acids of their phospholipids compared to a species in a warm environment |
C
|
A species in a cold environment will tend to have less double bonds in the fatty acids of their phospholipids compared to a species in a warm environment |
D
|
If the proportion of double bonds in a phospholipid increases, the fluidity of the membrane will decrease |
|
|
|
Tags:
Membrane Transport and Signalling | Lipids | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
The melting points (in degrees Celsius) of four different unsaturated 18-carbon fatty acids are as such: 70, 20, -5, and -15. Which of the following best describes this trend? |
|
A
|
The melting point increases as the number of cis double bonds in the fatty acid increases
|
B
|
The melting point decreases as the number of cis double bonds in the fatty acid increases
|
C
|
The melting point increases as the number of trans double bonds in the fatty acid increases
|
D
|
The melting point is unaffected by the number and types of double bonds present within the fatty acids
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best describes the concept of an amphipathic molecule?
|
|
A
|
An amphipathic molecule has one positively charged region and one negatively charged region
|
B
|
An amphipathic molecule is branched, and with at least two branch points
|
C
|
An amphipathic molecule has one polar region and one nonpolar region
|
D
|
An amphipathic molecule has two different types of bonds
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Lipids | Membrane Transport and Signalling | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is best associated with steroid hormones? |
|
A
|
Steroid hormones are water-soluble
|
B
|
The effects of steroid hormones are mediated by binding to a soluble receptor protein
|
C
|
Steroid hormones are synthesized directly from amino acid precursors
|
D
|
The intracellular actions of steroid hormones are mediated by small peptides
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | Hormonal Regulation | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is correct in regard to the metabolism of fatty acids?
|
|
A
|
Acetyl-CoA is produced, which increases the rate of the Citric Acid Cycle
|
B
|
Acetyl-CoA is produced, which decreases the rate of the Citric Acid Cycle
|
C
|
Glucose 6-phosphate is produced, which increases the rate of the Citric Acid Cycle
|
D
|
Glucose 6-phosphate is produced, which decreases the rate of the Citric Acid Cycle
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Metabolism of Fatty Acids and Proteins | Lipids | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following would NOT effectively separate amino acids and fatty acids? |
|
A
|
Separating on the basis of the properties (charge and binding affinities) of amino groups.
|
B
|
Separating based on the reactivity of any carboxylic acid group present.
|
C
|
Separating in water on the basis of solubility differences.
|
D
|
Separating the two based on the difference in size and shape.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | Separation and Purification | Protein Structure and Function | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
In humans, which of the following does NOT contain bile? |
|
A
|
Liver |
B
|
Stomach |
C
|
Duodenum |
D
|
Gallbladder |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | Digestive System | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
What change is made to a triglyceride to convert it into a phospholipid? |
|
A
|
A phosphate group is replaced with a fatty acid chain. |
B
|
A phosphate group is added to the end of one of the fatty acid chains. |
C
|
A phosphate group is added to the central glycerol molecule. |
D
|
A fatty acid chain is replaced with a phosphate group. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
In eukaryotes, beta oxidation of fatty acids takes place at the: |
|
A
|
cytosol. |
B
|
mitochondria. |
C
|
golgi apparatus. |
D
|
plasma membrane of the cell. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is FALSE regarding fatty acids? |
|
A
|
Synthesis of fatty acids occurs in the liver. |
B
|
Fatty acids are mostly obtained by diet rather than construction by the body. |
C
|
Fatty acids are important for the structure of cell membranes. |
D
|
Unsaturated fatty acids have zero double bonds. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is an accurate statement regarding saturated fats? |
|
A
|
All available sites for bonded hydrogen atoms on carbon atoms are occupied. |
B
|
They contain at least one double bond between a carbon atoms along their chain. |
C
|
They lack long chains of carbon atoms. |
D
|
They have a lower melting point than unsaturated fats. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Lipids | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|

