|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
The transmission of F factor plasmids is facilitated by? |
|
A
|
transduction |
B
|
transposition |
C
|
conjugation |
D
|
transformation |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gram staining is a common technique utilized for classification of bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria, when stained, appear purple under the microscope, while Gram-negative bacteria do not. This provides a simple method to organize bacteria. The difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria is that |
|
A
|
Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria differ in receptor molecules on the cell membrane. Gram-positive bacteria have receptors that induce the translation of a purple gene. |
B
|
The bacteria have different thicknesses of the peptidoglycan cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria have a thicker cell wall thus the stain does not leave the cell once it has entered and reacted with the iodine solution. |
C
|
The bacteria have different hydrolytic enzymes that digest the stain molecules. |
D
|
The Gram-positive bacteria possesses a cell wall while the other does not. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
The site of oxidative metabolism in eukaryotes is the mitochondrion, which utilizes specialized membranes in order to generate ATP. What is the analogous structure in prokaryotes used to carry out oxidative metabolism? |
|
A
|
outer membrane |
B
|
plasma membrane |
C
|
nuclear membrane |
D
|
cell wall |
|
|
|
Tags:
Eukaryotic Cells | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
Organisms which can run metabolic pathways with or without the presence or absence of oxygen are called: |
|
A
|
facultative anaerobes |
B
|
obligate anaerobes |
C
|
obligate aerobes |
D
|
protoplasts |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular bacteria is noted to have a small plasmid, which is identified as coding for a sex pilus. If this plasmid is removed from all of the bacteria in a colony, what can be expected of the colony? |
|
A
|
Reproduction would desist and the colony would naturally die out. |
B
|
Population growth would slow down. |
C
|
Mutations would have a much more harmful effect on the colony. |
D
|
Population growth would remain the same. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not involved with Hfr strains of bacteria? |
|
A
|
Sex pilus |
B
|
Conjugation |
C
|
nucleosome |
D
|
F plasmid |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular organism is found to perform the electron transport chain across its plasma membrane. Which of the following is the most likely identity of the organism? |
|
A
|
plant |
B
|
fungus |
C
|
animal |
D
|
bacterium |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Lac operon contains three genes; Lac A, Lac Z, and Lac Y. A promoter lies upstream of the three genes. When IPTG, an inducer of the lac operon, indirectly exposes the promoter, which of the operon genes will be transcribed? |
|
A
|
none; only genes immediately adjacent to the promoter will be transcribed |
B
|
the first gene in the operon; all genes are controlled by their own individual promoters |
C
|
none; promoters do not control the transcription of genes on operons, only standalone genes |
D
|
all; all genes within a single operon are transcribed as a unit, as initiated by a single promoter |
|
|
|
Tags:
Genetic Code, Transcription, Translation | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
Lysozymes are a collection of enzymes which function by attacking peptidoglycans (found in the cells walls of bacteria) and hydrolyzing the glycosidic bond that connects N-acetylmuramic acid with the fourth carbon atom of N-acetylglucosamine (Wikipedia). Infants receive lysozyme through breast feeding. If infant formula is used to feed the child instead, what complications might be expected to arise? |
|
A
|
Increased likelihood of chickenpox if the child is not vaccinated. |
B
|
Digestive problems |
C
|
Increased susceptibility to salmonella. |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
Under a high amount of mutagen exposure, the SOS mechanism of replication in prokaryotes forces reproduction past the normal mitotic checkpoints regardless of mutations. Which of the following is a likely fate of the daughter cells derived from E. coli in an SOS reproduction mode? |
|
A
|
viability of only a single daughter cell due to isolation of mutated genes in one daughter cell |
B
|
no noticeable differences because the checkpoints were all passed |
C
|
a survival advantage due to gain-of-function mutations |
D
|
death due to high mutation rate in gene products |
|
|
|
Tags:
Mitosis and Meiosis | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gram's iodine allows crystal violet to form large complexes which are then retained in certain bacteria and released in other bacteria during decolorization. Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between Gram-staining bacteria, the thickness of their cell wall, and their outer membrane? |
|
A
|
Gram positive - thin cell wall - has an outer membrane |
B
|
Gram positive - thick cell wall - has no outer membrane |
C
|
Gram negative - thin cell wall - has no outer membrane |
D
|
Gram negative - thick cell wall - has an outer membrane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is involved in post-translational processing in prokaryotes?
|
|
A
|
Golgi Apparatus |
B
|
Ribosome |
C
|
Nucleus |
D
|
Prokaryotes do not perform post-translational processing |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Endospore formation is an example of |
|
A
|
Sexual reproduction |
B
|
Asexual reproduction |
C
|
Dormant survival |
D
|
Death |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
M. tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis, causes latent infection in a vast majority of infected patients. These latent infections are characterized by granulomas - small areas of infected tissue that are surrounded by immune cells in an attempt to contain the spread of the bacteria. These granulomas can persist indefinitely without progressing to the disease, leaving the patient unaware of his infection. Which of the following is the most likely reason for the formation of granulomas? |
|
A
|
The immune system is unable to eradicate the bacteria, so it walls them off to prevent their spreading. |
B
|
The bacteria induce formation of granuloma to protect themselves from the immune system. |
C
|
The immune system retains the latent infection to prevent opportunistic infection from other, more destructive bacteria. |
D
|
The bacteria go into dormancy; dormant bacteria cannot be removed by the immune system, thereby resulting in granuloma formation. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Immune System | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
You want to obtain a spontaneous mutant for Ampicillin resistance in a sample of E. coli. Of the strategies listed below, which is most likely to yield a result the fastest? |
|
A
|
Plate the E. coli on medium with 1 g/mL Ampicillin |
B
|
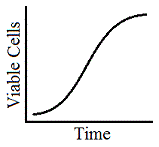
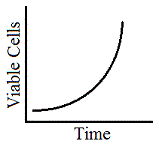
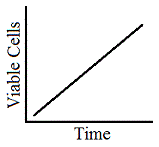
Plate the E. coli on medium with 1 μg/L Ampicillin |
C
|
Plate the E coli on a linear gradient medium from a concentration of 1μg/L to a 1 g/mL. |
D
|
None; the rise of spontaneous mutants is random and cannot be controlled by any of the methods listed |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
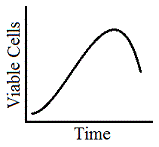
Observe the following growth curve for a yeast in fresh medium.
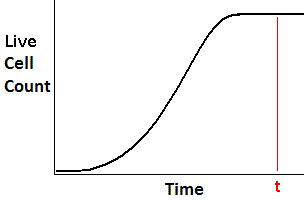
Which of the following statements is true about the growth of the yeast at time = t? |
|
A
|
There is no cell growth |
B
|
There is no cell division |
C
|
There is no cell death |
D
|
Cell division = cell death |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
To which of the following antibacterial methods would
you expect a bacterium be unable to develop resistance
assuming it was not resistant before?
I. Quinolone
II. Macrolide
III. 70% Ethanol
IV. Boiling |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
II, III, and IV only |
C
|
III and IV only |
D
|
I, II, III, and IV |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
A man suffers from an E. coli (gram negative) infection. After taking antibiotics, blood tests indicate that the E. coli infection are dead. However, the man soon develops a high fever and inflammation. This is most likely due to
|
|
A
|
the peptidoglycan of the cell wall
|
B
|
the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of the outer membrane
|
C
|
the flagellin from the flagella
|
D
|
the E. coli spores that evaded detection and later germinated
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Immune System | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Horizontal gene transfer occurs when one organism receives genetic material from another organism without being a descendant of the organism. Which of the following describes horizontal gene transfer? |
|
A
|
Cell A is produced by mitosis from Cell B which is produced by mitosis from Cell C. Cell A has genes from Cell C. |
B
|
Cell A is produced by mitosis from Cell B. Cell A has genes from Cell B. |
C
|
Cell A and Cell Z are in different kingdoms. Cell Z inserts genes into Cell A. |
D
|
Cell A and Cell Z are in different kingdoms. The two cells share a gene through ancestral decent. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Viruses | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
F factor plasmids are transferred through |
|
A
|
transformation |
B
|
conjugation |
C
|
transduction |
D
|
transposition |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
Fermentation of recombinant eukaryotic proteins is often done in prokaryotes. Which of the following is not a problem or risk associated with using prokaryotic systems for expression of eukaryotic proteins? |
|
A
|
Prokaryotes do not post-translationally modify their proteins and cannot perform glycosylation or specialized folding tasks. |
B
|
Prokaryotes contain endotoxin which must be extracted thoroughly before it can be used for human applications. |
C
|
Prokaryotes may not use the same codons as found on the eukaryotic DNA and thus may not have certain tRNAs, resulting in premature termination of translation. |
D
|
Prokaryotes have a high frequency of integrating DNA into their chromosomes which blocks transcription almost entirely. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is most likely to be an effective, but not definitive, innate immune system assay for endotoxins like lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from a bacteria-derived sample? |
|
A
|
Injecting the sample into a rabbit and measuring rapid onset of fever and inflammation |
B
|
Feeding the sample to mice and testing for blood in the feces |
C
|
Adding the sample to an immortalized cell line of a mouse B lymphoma and measuring antibody output |
D
|
Adding the sample to a culture of E. coli and measuring growth inhibition |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Immune System | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which process involves transfer of DNA from a virus to a bacterium? |
|
A
|
Transcytosis |
B
|
Translation |
C
|
Transposition |
D
|
Transduction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Viruses | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
Competent bacteria cells are capable of taking up plasmids. A scientist in a lab intends to amplify a specific plasmid by transforming a competent strain of bacteria with the plasmid in question and then letting the bacteria divide. The scientist can then isolate the bacterial genetic material, which includes now includes the plasmid. The plasmid also encodes a gene for ampicillin resistance (which is not encoded in the competent bacteria cells), allowing transformed bacteria to grow on agar plates containing ampicillin. A negative control is used to determine if a confounding variable is affecting an experiment's results. Negative controls are groups in which we would not expect a result when applying all of the experiment`s conditions except for the independent variable. Which of the following can act as a negative control to ensure that the bacteria that grow on the agar containing ampicillin are transformed bacteria? |
|
A
|
Just distilled water |
B
|
Just competent bacteria cells |
C
|
Just plasmid |
D
|
Just bacterial cells and plasmid |
|
|
|
Tags:
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
Recombinant plasmids are used to clone gene fragments encoding desired proteins. They are constructed by cutting the plasmid vector (containing an ampicillin resistance gene) and gene insertion fragments with restriction enzymes such that the end fragments of the cut sites match with each other. The cut plasmid vector and insertion fragment are then ligated together with the enzyme ligase to form the recombinant plasmid. This recombinant plasmid can be transformed into competent bacteria and plated onto agar plates with ampicillin, where only bacterial colonies with the recombinant plasmids can grow. Colonies can then be picked and have their recombinant plasmids amplified via PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
In which the following experimental conditions will we not expect bacteria colonies to grow on agar plates with ampicillin?
|
|
A
|
Competent bacteria mixed with a plasmid vector which has been cut with two different restriction enzymes (resulting in nonidentical cut sites), and reacted with ligase. |
B
|
Competent bacteria mixed with uncut plasmid vector. |
C
|
Competent bacteria mixed with cut plasmid vector and insertion fragment with ligase. |
D
|
Competent bacteria mixed with plasmid vector cut with a single restriction enzyme and reacted with ligase. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following organisms would be expected to survive under anoxic conditions?
I. Obligate aerobe
II. Obligate anaerobe
III. Facultative anaerobe |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I and II only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
A strain of bacteria is transformed with a gene encoding for telomerase. This is most likely going to have which of the following effects on the bacterial strain? |
|
A
|
Increase life span by elongating the telomeres. |
B
|
Decrease life span by shortening the telomeres. |
C
|
It depends on the type of bacterium. |
D
|
No effect. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
Clostridium botulinum is a common soil bacterium. Unlike some other obligate anaerobes, C. botulinum is able to survive in the presence of oxygen with the help of certain metabolic antioxidants. Which of the following enzymes would you expect to find in C. botulinum that you would not find in non-aerotolerant anaerobes? |
|
A
|
pyruvate dehydrogenase (pyruvate → acetyl CoA) |
B
|
carbonic anhydrase (CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3) |
C
|
superoxide dismutase (O2- → H2O2) |
D
|
monoamine oxidase (RCH2NH2 ↔ RCHO) |
|
|
|
Tags:
Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, PPP | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular bacterial cell has a mutation in its genome such that it has a nonfunctional A-site in all of the ribosomes it produces. Such a mutation would result in which of the following? |
|
A
|
Increased production of protein within the cell |
B
|
Production of proteins lacking in disulfide bonds |
C
|
Complete inability to translate mRNA |
D
|
Increased speed of ribosomal denaturation in low pH environments |
|
|
|
Tags:
Genetic Code, Transcription, Translation | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
S. aureus is a ubiquitous microorganism found on human skin that can cause infection. Strains of the bacterium can be resistant to various common antibiotics including methicillin, making the infections particularly difficult to treat. This suggests that
I. antibiotic-resistant bacteria are more virulent than non-resistant bacteria
II. immunocompromised individuals are susceptible to infection by both antibiotic-resistant and non-resistant strains of S. aureus
III. an individual infected with non-resistant strains will not benefit from treatment with antibiotics |
|
A
|
II only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
The colon of the gastrointestinal system houses large amounts of enteric (or intestinal) bacteria. These bacteria serve a protective role in the body through amplification of the immune system and preventing foreign bacteria from populating the region. Given the environment within the colon, which of the following would not be a common feature seen in the bacteria? |
|
A
|
Production of lactate |
B
|
Glycolytic enzymes |
C
|
Inactive ETC proteins in facultative anaerobes |
D
|
All of the above would be found |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Digestive System | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
A bacterium releases an antigen which causes a localized inflammation response in a cut. The inflammation itself is a result of |
|
A
|
antigen aggregation stimulating bacterial evasive heating |
B
|
cytokine release by the host immune system |
C
|
increased volume of rapidly-replicating bacteria |
D
|
reduced blood flow to the cut site to prevent the infection from spreading to the bloodstream |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Immune System | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gram positive bacteria differ from gram negative bacteria in that they |
|
A
|
do not contain any peptidoglycan |
B
|
are resistant to penicillin |
C
|
have two membranes with a thin peptidoglycan coat |
D
|
contain a thicker peptidoglycan coat |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
Three drugs, called Drug A, B, and C, are created as anti-bacterial agents. Drug A is capable of splicing bacterial RNA segments. Drug B can insert frameshift mutations. Drug C acts via proteolytic cleavage within the bacteria. Which of the following can be deduced about these drugs? |
|
A
|
Drug B is unable to change cell-wall composition of the bacterium |
B
|
Drug A and Drug C can both at most affect one protein |
C
|
Drug C has the exact same action as trypsin |
D
|
Drug B will have a larger impact on the progeny of bacteria than Drug C |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
In performing a gram stain, gram positive bacteria will appear |
|
A
|
Clear because the decreased peptidoglycan in the bacteria makes it colorless |
B
|
Pink because the additional peptidoglycan in the cell wall allows the dye to stay in the cell |
C
|
Purple because the additional peptidoglycan in the cell wall allows the dye to stay in the cell |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
A new organism is identified to possess lipopolysaccharide. This organism must therefore be |
|
A
|
Gram positive bacterium |
B
|
Gram negative bacterium |
C
|
Eukaryote |
D
|
Fungus |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a defining feature that is unique to conjugation and not any other type of horizontal gene transfer? |
|
A
|
direct cell-to-cell contact |
B
|
transfer of genetic material from one organism to another |
C
|
transfer of genetic material through a viral intermediate |
D
|
uptake of a plasmid with antibiotic resistance |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
A bacterium has been genetically transformed with human Gene A which consists of approximately 800 nucleotides. During expression, researchers notice that the protein is not being translated; only fragments of approximately 50 amino acids are formed. Genetic sequencing shows there are no nonsense mutations in the gene sequence. Which of the following is a plausible explanation for the observation? |
|
A
|
The bacterium lacks the tRNA that corresponds to the particular codon for the 51st amino acid. |
B
|
The bacterial ribosome is incompatible with the human mRNA and cannot properly translate the protein. |
C
|
The bacterium is unable to glycosylate the protein, terminating translation early. |
D
|
The human gene is too long; bacteria can only synthesize proteins up to approximately 50 amino acids. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
Binary fission is an example of |
|
A
|
asexual reproduction. |
B
|
sexual reproduction. |
C
|
oogenesis. |
D
|
spermatogenesis. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following processes contributes most to genetic diversity among a population of bacterium? |
|
A
|
Conjugation |
B
|
Binary fission |
C
|
Transformation from a population of clones |
D
|
Asexual reproduction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Evolution | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
A drug disassembles microtubles in yeast. When a yeast is treated with this drug during mitosis, which phase of mitosis is most greatly affected? |
|
A
|
prophase |
B
|
metaphase |
C
|
anaphase |
D
|
telophase |
|
|
|
Tags:
Mitosis and Meiosis | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the best lead for a drug target against intracellular bacterial infection? |
|
A
|
Infection-specific bacterial protein |
B
|
Actin |
C
|
DNA |
D
|
Peptidoglycan |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following would be least likely to be associated with a prokaryotic cell? |
|
A
|
Mitotic spindle |
B
|
Peptidoglycan |
C
|
Plasmid |
D
|
Flagella |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
Antibiotic resistance can be transmitted between bacterial species occupying a particular niche. This acquisition represents a transmission of which of the following? |
|
A
|
nucleic cid |
B
|
protein |
C
|
cytosol |
D
|
lysosome |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
Acid-tolerant bacteria do not have a survival advantage in the small intestine because |
|
A
|
acid-tolerant bacteria are abundant in the small intestine. |
B
|
the small intestine produces a special type of acid to which these bacteria are susceptible. |
C
|
the small intestine targets acid-tolerant bacteria in other ways. |
D
|
the small intestine is not particularly acidic. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Digestive System | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
Certain antibiotics kill bacteria by inhibiting translation, directly affecting the ribosomes. These antibiotics are not also damaging to human cells because: |
|
A
|
human ribosomes are protected from antibiotics by being in the nucleus. |
B
|
human cells have enzymes that can degrade the antibiotics. |
C
|
the antibiotics are only capable of entering the bacterial cells. |
D
|
bacterial ribosomes are structurally different from human ribosomes. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes | Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
A blood sample is taken from a sick patient and sample is lysed. Out of the total lysate, peptidoglycan is detected. The patient has most likely been infected with which of the following? |
|
A
|
protist |
B
|
bacteria |
C
|
fungus |
D
|
parasitic worm |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
A researcher wants to insert a series of genes too large to be practically transferred by a plasmid. The researcher places them into a viral capsid and infects a bacterium with the virus. This method of gene transfer is known as: |
|
A
|
transformation |
B
|
transduction |
C
|
conjugation |
D
|
vertical gene transfer |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Viruses | |
|
| 49 |
Go |
Q:
|
Penicillin acts to inhibit the production of peptidoglycan. As a result, penicillin acts as an antibacterial by: |
|
A
|
osmotic lysis |
B
|
inhibition of translation |
C
|
disrupting membrane transport |
D
|
inhibition of DNA replication |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following incorrectly pairs a cellular process with the location in which that process occurs in a eukaryotic cell? |
|
A
|
translation, mitochondria |
B
|
glycosylation, endoplasmic reticulum |
C
|
Krebs cycle, mitochondrial intermembrane space |
D
|
fatty acid catabolism, peroxisome |
|
|
|
Tags:
Eukaryotic Cells | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 51 |
Go |
Q:
|
Where sanitation is a challenge, measles patients are often given antibiotics for skin infection. The purpose of the antibiotics is to: |
|
A
|
prevent the measles virus from spreading on the skin and becoming more infectious to others. |
B
|
limit viral replication and reduce the amount of time the patient is sick. |
C
|
prophylactically prevent skin rashes and wounds from becoming infected with opportunistic bacteria. |
D
|
reduce the pain and itch associated with the viral infection. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Viruses | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
A bacterium is being studied by a scientist who discovers that oxygen is lethal to the bacterium. Which of the following best explains the reason for this? |
|
A
|
The ATP produced by the organism's metabolism from exposure to oxygen floods the cell to overdose. |
B
|
The oxygen is consumed by oxygen-detecting metabolic reactions which induce bacterial suicide. |
C
|
The bacterium lacks enzymes for catalyzing reactive oxygen species into more benign compounds. |
D
|
The normal energy-producing reactions of the bacterium are outcompeted by the presence of oxygen and the cell is no longer able to produce energy. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 53 |
Go |
Q:
|
A researcher has an agar plate covered with a lawn of E. coli. She adds a drop of a unknown substance, and the next day there is a clear spot on the plate where the substance was added. This substance could be:
I. A virus undergoing the lytic cycle.
II. A virus undergoing the productive cycle.
III. A chemical that is toxic to prokaryotes. |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
III only |
C
|
I and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ergosterol is a steroid compound found in fungi which serves a similar function to cholesterol in animal cells. Ergosterol is also often detected in samples of various grasses. Which of the following experiments would best identify whether ergosterol is produced by the plants or is a contaminant in the plant samples? |
|
A
|
Compare ergosterol levels in fungus-contaminated seeds versus fresh seeds with no visible contamination. |
B
|
Harvest seeds at various time points throughout the season and measure changes in ergosterol over time. |
C
|
Transform fungal ergosterol-producing genes into plants and compare their ergosterol levels to the levels of unmodified plants. |
D
|
Supply plants with Amphotericin B, an antifungal which targets ergosterol in membranes. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Membrane Transport and Signalling | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following features is consistent with the classification of Gram positive bacteria? |
|
A
|
the cell lacks an outer membrane |
B
|
the cell wall contains mycolic acid |
C
|
the cell has a very thin cell wall of peptidoglycan |
D
|
the cell lacks ribosomes |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 56 |
Go |
Q:
|
A culture of broth media is prepared and inoculated with bacterial cells, then placed in a growth incubator. As time approaches infinity, which of the following graphs best depicts the number of viable cells in the culture? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gram staining is an important technique for identification of certain bacterial species. Gram positive and negative organisms appear differently with this stain under light microscopy. Gram positive appears purple whereas gram negative appear pink. The mechanism behind this is |
|
A
|
Gram negative organisms are able to enzymatically digest purple dye |
B
|
Gram positive organisms retain purple dye |
C
|
Gram positive organisms are unable to uptake the pink dye |
D
|
Gram negative organisms express protein allowing for pink dye binding |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 58 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following contains peptidoglycan?
I. Gram negative bacteria
II. Gram positive bacteria
III. shells of arthropods |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II only |
C
|
I and II |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 59 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ribosomes as molecular structures have been found to be highly evolutionarily conserved. It has been found that: |
|
A
|
prokaryotes and eukaryotes both have identical ribosome structures. |
B
|
prokaryotes do not have ribosomes. |
C
|
eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes are both composed of 2 subunits. |
D
|
eukaryotes and prokaryotes have similar ribosomes, however they are not used for translation in prokaryotes. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Evolution | Eukaryotic Cells | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 60 |
Go |
Q:
|
Lysozyme, an enzyme which degrades peptidoglycan of cell walls, would be most effective against which of the following? |
|
A
|
Gram-positive bacteria |
B
|
Gram-negative bacteria |
C
|
Protists |
D
|
Viruses |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 61 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT true regarding prokaryotes and eukaryotes? |
|
A
|
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes are bound by plasma membranes
|
B
|
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes use DNA as their genetic material
|
C
|
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles
|
D
|
While eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles, prokaryotes do not
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | Eukaryotic Cells | |
|
| 62 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following can NOT be classified as eukaryotic organisms? |
|
A
|
Plants |
B
|
Archaea |
C
|
Protists |
D
|
Fungi |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 63 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is FALSE for F- bacteria? |
|
A
|
F- bacteria act as the recipient in bacterial conjugation.
|
B
|
F- bacteria can form a pilus.
|
C
|
During conjugation, an F- strain can gain antibiotic resistance.
|
D
|
F- bacteria do not contain a fertility factor.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 64 |
Go |
Q:
|
A drug inhibiting cell division at anaphase would be most effective against which of the following? |
|
A
|
prokaryote |
B
|
virus |
C
|
eukaryote |
D
|
prion |
|
|
|
Tags:
Eukaryotic Cells | Prokaryotes | |
|
| 65 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Gram stain distinguishes what type of organisms? |
|
A
|
Pathogenic bacteria versus nonpathogenic bacteria. |
B
|
Bacteria with a single membrane and a thick layer of peptidoglycan versus bacteria with two membranes and a thin layer of peptidoglycan. |
C
|
Bacteria with a cell wall versus bacteria without a cell wall. |
D
|
Bacteria versus archaea. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 66 |
Go |
Q:
|
which of the following accurately depicts the difference between gram positive and gram negative bacteria? |
|
A
|
One has a capsule and one does not. |
B
|
One has two plasma membranes and one has only one. |
C
|
One has peptidoglycan in the cell envelope and one does not. |
D
|
One has a significant number of striations in the cellular membrane and one does not. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 67 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not a shape of bacteria? |
|
A
|
round |
B
|
spiral |
C
|
rod-shaped |
D
|
triangular |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 68 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is an incorrect statement regarding bacterial genetic transmission? |
|
A
|
Bacterial conjugation is an example of vertical gene transmission. |
B
|
Bacterial conjugation creates direct connections between cells for transfer of genetic information. |
C
|
Antibiotic resistance is a direct consequence of gene transfer between bacteria. |
D
|
Typically plasmids are transferred between bacteria during bacterial conjugation. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 69 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gram positive bacteria have cell walls primarily composed of: |
|
A
|
peptidoglycan. |
B
|
LPS (lipopolysaccharides) |
C
|
fat-based molecules. |
D
|
phospholipids of the bacterial cell wall. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 70 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not a property of transduction as it pertains to bacteria? |
|
A
|
direct contact between the cell donating and the cell receiving DNA |
B
|
utilization of a DNA-containing viral vector |
C
|
at times the foreign DNA is integrated into the bacterial host DNA |
D
|
foreign DNA insertion into a host bacterial cell |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 71 |
Go |
Q:
|
Often times in hospital settings, blood is obtained from patients to evaluate for growth of bacterial organisms. Blood can be drawn into aerobic and anaerobic containers. For one patient, growth is seen in both types of containers. Which of the following terms describes such an organism? |
|
A
|
obligate anaerobe |
B
|
facultative anaerobe |
C
|
commensal anaerobe |
D
|
symbiotic anaerobe |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 72 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following are not prokaryotic organisms? |
|
A
|
organism from the archaea domain |
B
|
yeast |
C
|
bacilli bacteria |
D
|
cocci bacteria |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 73 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following are prokaryotic domains?
I. archaea
II. bacteria
III. protista |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II only |
C
|
I and II only |
D
|
I, II and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 74 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding gram positive bacteria?
I. it contains no mitochondria
II. it has a thick peptidoglycan layer
III. it lacks a plasma membrane |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II only |
D
|
I, II and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 75 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is false regarding binary fission? |
|
A
|
two daughter cells are produced in the process |
B
|
it utilizes a spindle apparatus to separate daughter DNA molecules |
C
|
it is commonly performed by prokaryotes |
D
|
it is a form of asexual reproduction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
| 76 |
Go |
Q:
|
F factor as it relates to bacteria refers to: |
|
A
|
a plasmid contained within F- bacteria. |
B
|
a cell-wall protein contained by bacteria which reproduce sexually. |
C
|
a specific plasmid which codes for a sex pilus. |
D
|
a particular DNA polymerase molecule found within asexual bacteria. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Prokaryotes | |
|
|
We can teach you how to crush the MCAT!
Learn More
|